What is the cerebrum responsible for?
The largest part of the brain, the cerebrum initiates and coordinates movement and regulates temperature. Other areas of the cerebrum enable speech, judgment, thinking and reasoning, problem-solving, emotions and learning. Other functions relate to vision, hearing, touch and other senses.
What is the function of the cerebellum and cerebrum?
Your cerebrum sends the signals to the muscles in your arms, and your cerebellum helps calculate and control your movements, so your hand goes right to the pencil without missing. Your cerebellum not only manages conscious thoughts, but also planning and actions.
Why does the cerebellum look different?
The unusual surface appearance of the cerebellum conceals the fact that most of its volume is made up of a very tightly folded layer of gray matter: the cerebellar cortex. Each ridge or gyrus in this layer is called a folium.
What does the cerebellum control quizlet?
The cerebellum, which stands for “little brain”, is a structure of the central nervous system. It has an important role in motor control, with cerebellar dysfunction often presenting with motor signs. In particular, it is active in the coordination, precision and timing of movements, as well as in motor learning.
What does the cerebellum control?
The cerebellum is primarily responsible for muscle control, including balance and movement. It also plays a role in other cognitive functions such as language processing and memory.
What is the information of the brain?
The brain is the most complex part of the human body. This three-pound organ is the seat of intelligence, interpreter of the senses, initiator of body movement, and controller of behavior. Lying in its bony shell and washed by protective fluid, the brain is the source of all the qualities that define our humanity.
What is the function of the cerebellum in memory?
The cerebellum plays a role in processing procedural memories, such as how to play the piano. The prefrontal cortex appears to be involved in remembering semantic tasks.
What are the functional areas of the cerebellum?
There are three functional areas of the cerebellum – the cerebrocerebellum, the spinocerebellum and the vestibulocerebellum.
How to improve cerebellum function?
Engaging in exercises such as yoga, dance, or martial arts can effectively engage the cerebellum. This can lead to enhanced neural connectivity among ADHD-associated circuits and lead to cognitive improvements. Exercise could potentially improve attention and working memory performance in those with ADHD.
What happens if your cerebellum is too big?
A Chiari malformation is a problem in which a part of the brain (the cerebellum) at the back of the skull bulges through a normal opening in the skull where it joins the spinal canal. This puts pressure on parts of the brain and spinal cord, and can cause mild to severe symptoms.
What happens if the cerebellum is damaged?
Damage to the cerebellum can lead to: 1) loss of coordination of motor movement (asynergia), 2) the inability to judge distance and when to stop (dysmetria), 3) the inability to perform rapid alternating movements (adiadochokinesia), 4) movement tremors (intention tremor), 5) staggering, wide based walking (ataxic gait …
What part of the brain controls memory?
Most available evidence suggests that the functions of memory are carried out by the hippocampus and other related structures in the temporal lobe.
What is the primary role of the cerebellum?
The cerebellum, one of three main parts that make up your brain, is responsible for coordinating movement and balance. Also known as the “little brain,” it plays a vital role in language and attention and can assist people with vision and eye movement.
What is the cerebellum not responsible for?
While the cerebellum is not thought to initiate movement, this part of the brain helps organize all of the actions of the muscle groups involved in a particular movement to ensure that the body is able to produce a fluid, coordinated movement.
How to cure cerebellum damage?
There is no cure for hereditary forms of cerebellar degeneration. Treatment is usually supportive and is based on the person’s symptoms or on disorders that may contribute to the cerebellar degeneration. Clinical trials are studies that allow us to learn more about disorders and improve care.
How does the cerebellum affect emotions?
According to the dysmetria of thought theory, the cerebellum provides accuracy, consistency and appropriateness to cognitive and affective functions, as it does for movement-related operations.
What is the cognitive role of the cerebellum?
It has an active role in a variety of mental activities, including facial recognition, emotion attribution, theory of mind attributions, directed attention, and many types of memory [49, 117–123]. In functional imaging studies, cerebellar activations occur even when motor components of the tasks are well-controlled.
What does the cerebellum of the brain control?
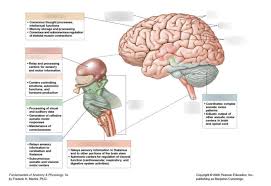
The portion of the brain in the back of the head between the cerebrum and the brain stem. The cerebellum controls balance for walking and standing, and other complex motor functions. Anatomy of the brain, showing the cerebrum, cerebellum, brain stem, and other parts of the brain.
How does the brain take information?
Information is delivered into the spinal cord through the axon terminals of sensory neurons. Once in the spinal cord, the information may flow to motor neurons, to interneurons that pass it directly to motor neurons, or to interneurons that transmit the information to the brain.
What are the functions of the cerebrum and cerebellum?
It performs higher functions like interpreting touch, vision and hearing, as well as speech, reasoning, emotions, learning, and fine control of movement. Cerebellum: is located under the cerebrum. Its function is to coordinate muscle movements, maintain posture, and balance.
What information is stored in the cerebellum?
In addition to its role in motor functions, the cerebellum also plays a significant role in emotional learning, pain processing, and the expression of verbal emotions, among other functions (Adamaszek et al., 2017).
What happens to memory if the cerebellum is damaged?
Cerebellar damage produces selective deficits in verbal working memory.
Is cerebellum a working memory?
These results are consistent with our current findings and are in line with the idea that cerebellum plays a predictive role in verbal working memory and in language comprehension through prediction of phonological information.
What is the physiology of the cerebellum?
The cerebellum is a relatively small part of human neuroanatomy with regards to size, however it plays a vital role in function and mobility. Traditionally known functions of the cerebellum include: Motor movement regulation to include movement and gait coordination and maintenance of posture. Balance control.
What is the cerebellum explained?
Your cerebellum is part of your brain that helps coordinate and regulate a wide range of functions and processes in both your brain and body. While it’s very small compared to your brain overall, it holds more than half of the neurons (cells that make up your nervous system) in your whole body.
What are the connections between the cerebellum?
The connections between the cerebellum and other parts of the nervous system occur by way of three large pathways called cerebellar peduncles (Figures 19.1 to 19.3). The superior cerebellar peduncle (or brachium conjunctivum) is almost entirely an efferent pathway.
What is the main point of the cerebrum?
Cerebrum. The cerebrum is the largest part of the brain. It consists of the cerebral cortex and other subcortical structures. It is composed of two cerebral hemispheres that are joined together by heavy, dense bands of fibre called the corpus callosum.
Which of the following functions is the cerebrum responsible for?
The cerebrum represents one of the largest regions of the brain as seen in Fig. 3, and its functions are critical for survival. It is responsible for processing information associated with movement, smell, sensory perception, language, communication, memory, and learning.
Does cerebrum protect the brain?
The brain is protected by the bones of the skull and by a covering of three thin membranes called meninges. The brain is also cushioned and protected by cerebrospinal fluid. This watery fluid is produced by special cells in the four hollow spaces in the brain, called ventricles.
What is the cerebrum responsible for quizlet?
The cerebrum constitutes the largest part of the human brain. It is also known as the cortex and is responsible for performing a great number of important brain functions, including action and thought processing.
What information does the cerebellum receive?
Where is the cerebellum located in the brain?
Why is it called a cerebellum?
How many parts of the cerebellum are there?
The cerebellum, that little brain tucked away at the back of your head, is a powerhouse of coordination and movement. It doesn’t just control our motor skills; it actually fine-tunes them, making sure our movements are smooth, accurate, and precise. But how does it do all that?
Well, the cerebellum relies on a constant stream of information from various parts of the brain and body. Think of it like a conductor of a symphony, receiving input from every instrument and orchestrating the perfect performance.
Let’s dive into the sources of information that the cerebellum depends on:
The Cerebral Cortex: The Master Plan
The cerebral cortex is the brain’s outermost layer, responsible for higher-level functions like planning, decision-making, and conscious thought. It’s where our intentions to move are born.
When we decide to pick up a coffee mug, for example, the cerebral cortex generates the initial plan of action. This plan is then relayed to the cerebellum through the pontine nuclei, a relay station in the brainstem.
The Spinal Cord: The Sensory Feedback Highway
The spinal cord acts as the communication highway between the brain and the body. It carries sensory information from the muscles, tendons, joints, and skin, constantly updating the cerebellum on the body’s position and movement. This feedback is crucial for the cerebellum to adjust movements in real-time.
Imagine you’re trying to balance on one foot. The spinal cord sends signals about your body’s position, the shifting of your weight, and any subtle movements. The cerebellum analyzes this information and makes tiny adjustments to your leg muscles, preventing you from toppling over.
The Vestibular System: The Inner Compass
Located in the inner ear, the vestibular system is our internal compass, keeping track of our head’s position and movement in space. It’s responsible for our sense of balance and spatial orientation.
When we spin around, for instance, the vestibular system detects the movement and sends signals to the cerebellum. The cerebellum uses this information to coordinate our eye movements, preventing dizziness and maintaining a stable visual field.
The Brainstem: The Communication Hub
The brainstem is the base of the brain, connecting it to the spinal cord. It’s a vital communication hub, relaying information from various parts of the body to the cerebellum and vice-versa.
The brainstem also houses important structures involved in controlling vital functions like breathing, heart rate, and sleep. It’s constantly sending information to the cerebellum, ensuring that our movements are smooth and coordinated, even while we’re sleeping.
The Cerebellum: The Orchestrator
The cerebellum integrates all this incoming information from the cerebral cortex, spinal cord, vestibular system, and brainstem. It compares the intended movement with the actual movement, detects any discrepancies, and sends signals to the motor cortex to fine-tune the movement.
This feedback loop allows the cerebellum to adjust our movements in real-time, ensuring accuracy, smoothness, and fluidity. It’s like a conductor constantly adjusting the tempo and volume of the symphony, creating a harmonious and flawless performance.
The Importance of Information Flow
The cerebellum’s ability to receive and process information from multiple sources is essential for our ability to move and interact with the world. Imagine trying to walk, write, or even talk without the cerebellum’s constant guidance. It would be a chaotic mess!
Here are some examples of how the cerebellum’s reliance on information from different sources plays a crucial role in our everyday lives:
Learning a new skill: When we learn a new skill, like playing a musical instrument or riding a bike, the cerebellum receives information about our movements and makes adjustments based on feedback. Over time, the cerebellum creates a motor program for the skill, allowing us to perform it smoothly and automatically.
Maintaining balance: The cerebellum constantly receives information from the vestibular system and spinal cord, allowing us to maintain our balance. This is crucial for tasks like walking, standing, and navigating our surroundings.
Performing complex movements: The cerebellum is involved in coordinating complex movements, like throwing a ball or playing a video game. It receives information about our intended movement, the position of our limbs, and the feedback from our muscles, allowing us to perform these actions with precision and accuracy.
What Happens When the Cerebellum Is Damaged?
When the cerebellum is damaged, it can lead to a range of problems affecting motor coordination, balance, and movement. This is called cerebellar ataxia. Symptoms of cerebellar ataxia can include:
Clumsy movements: Difficulty coordinating and controlling movements, leading to clumsiness and a lack of precision.
Tremors: Uncontrollable shaking or trembling of the limbs, especially during voluntary movements.
Balance problems: Difficulty maintaining balance and a tendency to fall.
Speech problems: Difficulty speaking clearly and smoothly, resulting in slurred speech.
Nystagmus: Involuntary, rapid eye movements.
FAQs About the Cerebellum
Q: What is the cerebellum’s role in learning and memory?
A: The cerebellum plays a role in motor learning and memory. It helps us learn new motor skills, like riding a bike or playing an instrument, by refining and storing motor programs.
Q: How does the cerebellum contribute to our sense of timing?
A: The cerebellum is involved in our sense of timing. It receives information about the duration of movements and events, helping us to coordinate our actions and movements with the timing of the environment.
Q: Is the cerebellum only involved in motor functions?
A: While the cerebellum is primarily known for its role in motor control, recent research suggests it might also be involved in higher-level cognitive functions, including language, attention, and working memory.
The cerebellum is a fascinating and complex part of the brain. Its ability to receive and integrate information from multiple sources makes it essential for our ability to move, learn, and interact with the world around us. So next time you reach for a cup of coffee, take a moment to appreciate the intricate dance of information that makes this seemingly simple act possible.
See more here: What Is The Function Of The Cerebellum And Cerebrum? | The Cerebellum Relies On Information From
Cerebellum: Definition, Location, and Functions
The cerebellum receives information from other regions of the brain and nervous system including the brain stem, spinal cord, Verywell Mind
Neuroanatomy, Cerebellum – StatPearls – NCBI
The cerebellum is a vital component in the human brain as it plays a role in motor movement regulation and balance control. National Center for Biotechnology Information
Cerebellum – Physiopedia
The cerebellum is located at the base of the brain, under the cerebrum and posterior to the spinal cord. The cerebellum is a relatively small part of human neuroanatomy with regards to size, however it plays a vital Physiopedia
Cerebellum Function, Anatomy & Definition | Body Maps – Healthline
The cerebellum receives information from the sensory systems, the spinal cord, and other parts of the brain and then regulates control of movements. Healthline
Cerebellum: What It Is, Function & Anatomy – Cleveland Clinic
Your cerebellum is a part of your brain located at the back of your head, just above and behind where your spinal cord connects to your brain itself. The name Cleveland Clinic
Cerebellum: Anatomy, function, and disorders
The cerebellum is the lower-back part of the brain. It only accounts for around 10% of total brain weight but contains as many as 80% of all neurons in the brain. The cerebrum participates in… Medical News Today
Cerebellum | Description, Anatomy, & Functions | Britannica
The cerebellum integrates nerve impulses from the labyrinths of the ear and from positional sensors in the muscles; cerebellar signals then determine the extent and Britannica
The Cerebellum – Structure – Position – Vasculature
Written by Sara Venturini. Last updated December 16, 2022 • 36 Revisions •. The cerebellum, which stands for “little brain”, is a structure of the central nervous system. It has an important role in TeachMeAnatomy
The Cerebellum | Principles of Neural Science, 6e
First, the cerebellum acts in advance of sensory feedback arising from movement, thus providing feedforward control of muscular contractions. Second, to achieve such control, AccessNeurology
See more new information: charoenmotorcycles.com
2-Minute Neuroscience: Cerebellum
Neurology | Cerebellum Anatomy \U0026 Function
Exciting New Developments In Cognitive Neuroscience Of The Cerebellum
What Is The Cerebellum?
Anatomy Of The Cerebellum
What Does The Cerebellum Do?
How The Cerebellum Controls Movement
The Cerebellum
Cerebellar Disease Symptoms
Link to this article: the cerebellum relies on information from.
See more articles in the same category here: https://charoenmotorcycles.com/how