What are the different types of perivascular spaces?
type 1: located in the area supplied by the lenticulostriate arteries entering the basal ganglia. type 2: located in the area supplied by the perforating medullary arteries as they enter the cortical grey matter. type 3: located in the midbrain.
What is a prominent Virchow Robin space?
The space created between the vessels and aforementioned leptomeningeal layer is considered the perivascular space (Figure 4), also known as Virchow–Robin spaces. These spaces extend primarily around the arteriolar vascular tree peripherally as far as the capillaries, where they begin to fenestrate.
What is dilation of Virchow-Robin spaces?
Dilatation of VRS results in fluid filled perivascular spaces along the course of the penetrating arteries. Abnormal dilatation of VRS is clinically associated with aging, dementia, incidental WM lesions, and hypertension and other vascular risk factors (2, 5).
What does a dilated perivascular space mean?
In humans, perivascular spaces surround arteries and veins can usually be seen as areas of dilatation on MRI images. While many normal brains will show a few dilated spaces, an increase in these spaces may correlate with the incidence of several neurodegenerative diseases, making the spaces a topic of research.
What causes an increase in perivascular space?
High blood pressure, age, or nonspecific inflammation can damage the endothelial cells of the blood vessels and disrupt the tight connections between endothelial cells, resulting in increased BBB permeability. This increases the amount of material leaking from blood vessels, which causes perivascular spaces to widen.
What are the spaces of Virchow?
The Virchow-Robin (VR) space is named after Rudolf Virchow (German pathologist, 1821–1902) (,1) and Charles Philippe Robin (French anatomist, 1821–1885) (,2). VR spaces, or perivascular spaces, surround the walls of vessels as they course from the subarachnoid space through the brain parenchyma.
How do you treat prominent perivascular spaces?
Treatment and prognosis No treatment is required provided that they are recognized as perivascular spaces. Change in the size of the cyst or presence of enhancement should make one doubt the diagnosis. In some instances, particularly those with increasing edema, a biopsy may be required to exclude a tumor.
What is the significance of Virchow?
Virchow’s greatest accomplishment was his observation that a whole organism does not get sick—only certain cells or groups of cells. In 1855, at the age of 34, he published his now famous aphorism “omnis cellula e cellula” (“every cell stems from another cell”).
Does everyone have perivascular spaces?
In adults, the presence of PVSs has been mainly linked to the aging process9 and to vascular and Alzheimer dementias. Two studies in youth concluded that in this population, PVSs were either absent or a rare finding, present in <5% of subjects.
What is the area of a dilated image?
Steps for How to Find the Area of the Figure After Dilation Step 1: Compute the area of the figure before dilation, . Step 2: Multiply the area of the figure before dilation, , by the square of the scale factor, . That is, the area of the figure after dilation, , is given by the equation A d = s 2 A p .
What is a dilation centered?
Dilation: A dilation is a stretch or a shrink in the size and location of a figure or point. Scale Factor: The scale factor in a dilation is the amount by which the figure is stretched or shrunk. Center of Dilation: The center of dilation is a reference point used to appropriately scale the dilation of a figure.
What is dilation of the venous system?
Gross venous dilatation is a characteristic of non-ischaemic retinal vein occlusion and indicates an increase in venous intraluminal pressure that would favour outward leakage of fluid from affected vessels so that both the effects of hypoxia and of hydrostatic stress are likely to be involved in the production of the …
What are the prominent Virchow-Robin spaces?
Virchow-Robin spaces are perivascular fluid-filled cavities that surround perforating arteries and veins in the brain parenchyma. As a rule in healthy people they are approximately 5 mm in diameter.
What is dilation of vessels in brain?
In the brain, if a certain neuron needs more nutrients, it will release signalling molecules that will cause the tiny muscles around a nearby blood vessel to relax. This widens (dilates) the vessel, increasing the blood flow and local nutrient availability.
What are Type 2 perivascular spaces?
Type II PVSs are found along the path of perforating medullary arteries as they enter cortical gray matter over the high convexities, extending into the white matter (Fig 2B). These spaces often asymmetrically involve one hemisphere.
What is a dilated perivascular space?
Enlarged perivascular spaces (EPVS), or Virchow-Robin spaces, are cerebrospinal fluid-filled cavities that surround small penetrating cerebral arterioles and correspond with extensions of the subarachnoid space.
Can perivascular spaces cause headaches?
Migraine and headache have both been associated with increased number of dilated perivascular spaces (PVS) on magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) in four clinic-based studies (1–4).
What is CSF in perivascular space?
The flow of cerebrospinal fluid along perivascular spaces (PVSs) is an important part of the brain’s system for delivering nutrients and eliminating metabolic waste products (such as amyloid-β); it also offers a pathway for the delivery of therapeutic drugs to the brain parenchyma.
What is the rule of Virchow?
Virchow’s law The observation that, during craniosynostosis, skull growth is restricted to a plane perpendicular to the affected, prematurely fused suture and is enhanced in a plane parallel to it.
What did Virchow suggest?
Virchow used the theory that all cells arise from pre-existing cells to lay the groundwork for cellular pathology, or the study of disease at the cellular level. His work made it more clear that diseases occur at the cellular level.
What is Virchow famous for?
Virchow is credited with several key discoveries. His most widely known scientific contribution is his cell theory, which built on the work of Theodor Schwann. He was one of the first to accept the work of Robert Remak, who showed that the origin of cells was the division of pre-existing cells.
Why is the perivascular space important?
Perivascular Spaces PVS are small fluid-filled spaces within white matter, which appear isointense to static CSF-filled regions on structural imaging. These spaces coincide with arterial trajectories, and excess size, number, or asymmetry may be a marker for neurologic disorders such as epilepsy.
What are the symptoms of tumefactive perivascular spaces?
Patients can present with nonspecific symptoms such as headache, dizziness, visual changes, balance disturbance, and so forth, but causation has not been established between tumefactive perivascular spaces and this varied symptomatology, and more often they are incidental findings.
What did Virchow determine?
Virchow’s research at Würzburg helped to establish the concept of cellular pathology, the idea that all diseases are caused by changes in normal cells. Virchow argued that life was merely the sum of the processes of cellular activities.
What is the triad of Virchow?
The three factors of Virchow’s triad include intravascular vessel wall damage, stasis of flow, and the presence of a hypercoagulable state.
What is Virchow’s lymph node?
Virchow’s node, a left supraclavicular lymph node, was first described by German pathologist Rudolf Ludwig Karl Virchow (1821-1901) in 1848 as a sign of metastatic malignancy mainly from gastric cancer.
What are the different types of perivascular dermatitis?
Among the inflammatory dermatoses, superficial perivascular dermatitis is an important pathological type with four subtypes: simplex, interface, psoriasiform and spongiotic (2).
What are the perivascular lymph spaces?
PVS, also known historically as Virchow-Robin spaces, surround vessels in the brain. These spaces act as a conduit for glymphatic fluid. The glymphatic fluid system is analagous to the lymphatic system and is mostly active during sleep, when it clears waste products such as amyloid β from the brain.
What is the difference between paravascular and perivascular space?
Paravascular flow is hypothesized to move inward to the brain tissue between astrocyte end feet and pia mater. Perivascular flow is hypothesized to move outward from the brain tissue in basement membranes between smooth muscle cells.
What is the difference between a lacune and a perivascular space?
Lacunes are small, fluid-filled cavities frequently seen on brain imaging in elderly individuals, indicating a healed stage of small deep brain infarcts or hemorrhage. Perivascular spaces (PVSs) are another kind of fluid-filled cavity commonly seen in elderly people with disparate pathological features [1].
What is a Virchow-Robin space?
Do MR images show dilatation of perivascular spaces?
Are Virchow-Robin spaces a neuroradiologic marker of inflammatory changes?
Is Virchow-Robin space a path of spread in neurosarcoidosis?
Hey there! Today, we’re diving into the fascinating world of dilated Virchow-Robin spaces (VRS), a topic that often pops up in radiology reports.
For those of you who aren’t familiar, Virchow-Robin spaces are small, fluid-filled spaces in the brain that surround blood vessels. They’re named after the German pathologist, Rudolf Virchow, and the French neurologist, Charles Robin.
Now, when these spaces get dilated, it means they’re larger than normal. This dilation can be a sign of something going on in the brain, but it’s not always a cause for alarm.
Understanding the Basics
Think of Virchow-Robin spaces like tiny pockets of fluid that act as cushions for the blood vessels that nourish the brain. They’re typically small, but they can become larger, especially as we age.
So, what does dilated Virchow-Robin spaces mean? It essentially means that these “cushions” have expanded, which could be a sign of:
Normal aging: As we age, these spaces can naturally enlarge.
High blood pressure: Chronic high blood pressure can put stress on blood vessels, leading to dilation of VRS.
Microvascular disease: Conditions affecting the tiny blood vessels in the brain, like cerebral amyloid angiopathy, can lead to VRS dilation.
Brain injury: Traumatic brain injuries or strokes can cause VRS dilation.
How do we see dilated Virchow-Robin spaces?
Dilated Virchow-Robin spaces are usually detected on brain imaging studies like:
MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging): MRI is often the gold standard for visualizing VRS.
CT Scan (Computed Tomography Scan): CT scans can also show VRS, though sometimes not as clearly as an MRI.
These imaging studies provide detailed snapshots of the brain, allowing radiologists to spot any abnormalities like dilated Virchow-Robin spaces.
What does it mean if you have dilated Virchow-Robin spaces?
The significance of dilated Virchow-Robin spaces depends on several factors, including:
The size of the spaces: Larger spaces are more likely to be associated with underlying conditions.
Location of the spaces: Certain areas of the brain are more prone to VRS dilation than others.
Patient’s age: VRS dilation is more common in older individuals.
Presence of other symptoms: If you have symptoms like headaches, dizziness, or memory problems, it’s important to tell your doctor.
When should you be concerned about dilated Virchow-Robin spaces?
While dilated Virchow-Robin spaces are usually harmless, it’s essential to be aware of potential concerns:
Cognitive decline: In some cases, dilated Virchow-Robin spaces can be associated with mild cognitive impairment or dementia.
Stroke risk: Conditions that can lead to dilated Virchow-Robin spaces, such as high blood pressure or microvascular disease, can also increase the risk of stroke.
Other neurological symptoms: If you experience any neurological symptoms, such as headaches, seizures, or vision problems, it’s crucial to consult your doctor promptly.
What can I do if I have dilated Virchow-Robin spaces?
If you’re diagnosed with dilated Virchow-Robin spaces, your doctor will typically recommend a few steps:
Regular checkups: Your doctor will likely want to monitor your condition with regular checkups.
Lifestyle changes: Modifying lifestyle factors like diet, exercise, and smoking cessation can improve overall health and potentially reduce the risk of complications.
Management of underlying conditions: If you have high blood pressure, diabetes, or other health issues, it’s crucial to manage these effectively to minimize the impact on your brain health.
A Final Note
It’s important to remember that dilated Virchow-Robin spaces are not always a cause for alarm. However, it’s always best to discuss any findings on your brain imaging with your doctor to get personalized advice and ensure you understand the potential implications.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What is the difference between dilated Virchow-Robin spaces and white matter lesions?
Both dilated Virchow-Robin spaces and white matter lesions can be seen on brain imaging, but they’re different entities. Dilated Virchow-Robin spaces are fluid-filled spaces around blood vessels, while white matter lesions are areas of damage or injury to the brain’s white matter, which carries signals between different parts of the brain.
2. Can dilated Virchow-Robin spaces be treated?
There’s no specific treatment for dilated Virchow-Robin spaces. However, managing underlying conditions like high blood pressure and diabetes can help slow the progression of VRS dilation and potentially reduce the risk of complications.
3. What are the symptoms of dilated Virchow-Robin spaces?
Many people with dilated Virchow-Robin spaces have no symptoms. However, in some cases, it can be associated with headaches, dizziness, cognitive impairment, or other neurological symptoms.
4. Can dilated Virchow-Robin spaces cause dementia?
Dilated Virchow-Robin spaces themselves don’t directly cause dementia. However, conditions that can lead to VRS dilation, such as cerebral amyloid angiopathy, are also linked to an increased risk of dementia.
5. Should I be worried if I have dilated Virchow-Robin spaces?
Whether you should be worried about dilated Virchow-Robin spaces depends on the size, location, and any associated symptoms. It’s important to discuss the findings with your doctor to get personalized advice.
6. Can dilated Virchow-Robin spaces go away?
Dilated Virchow-Robin spaces are usually permanent, but they may not worsen significantly. Lifestyle modifications and management of underlying conditions can help prevent further dilation.
7. How common are dilated Virchow-Robin spaces?
Dilated Virchow-Robin spaces are quite common, particularly in older individuals. They’re often detected during routine brain imaging, and many people with VRS dilation are asymptomatic.
8. Can I prevent dilated Virchow-Robin spaces?
While you can’t completely prevent VRS dilation, adopting healthy lifestyle habits can help reduce the risk. These include maintaining a healthy weight, managing blood pressure, controlling blood sugar levels, and quitting smoking.
9. What happens if dilated Virchow-Robin spaces are not treated?
Dilated Virchow-Robin spaces themselves don’t require treatment, but managing any underlying conditions is crucial. Untreated high blood pressure, diabetes, or other health issues can worsen VRS dilation and increase the risk of complications.
10. What is the difference between dilated Virchow-Robin spaces and perivascular spaces?
Dilated Virchow-Robin spaces and perivascular spaces are essentially the same thing. They’re fluid-filled spaces surrounding blood vessels in the brain. The terms are often used interchangeably.
We hope this exploration of dilated Virchow-Robin spaces has provided you with a clearer understanding of this topic. Always remember to talk to your doctor if you have any concerns about your health or your brain imaging findings.
See more here: What Is A Prominent Virchow Robin Space? | Dilated Virchow Robin Spaces Radiology
Dilated Virchow-Robin spaces | Radiology Case | Radiopaedia.org
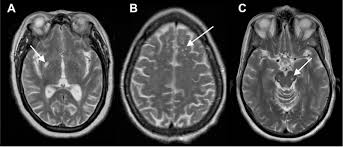
MR images show marked dilatation of perivascular spaces (Virchow-Robin) that involved basal ganglia (thalami and lenticular nuclei) without associated mass effect. These follow Radiopaedia
Neuroimaging of Dilated Perivascular Spaces: From Benign and
Perivascular spaces (PVSs), also known as Virchow-Robin spaces, are pial-lined, fluid-filled structures found in characteristic locations throughout the brain. They can become National Center for Biotechnology Information
Virchow-Robin Spaces at MR Imaging | RadioGraphics
Virchow-Robin (VR) spaces surround the walls of vessels as they course from the subarachnoid space through the brain parenchyma. Small VR spaces appear in all age groups. With RSNA Publications Online
Dilated Virchow-Robin spaces | Radiology Case | Radiopaedia.org
Dilated Virchow-Robin spaces. mri. There is a right well-circumscribed fluid-filled cyst of CSF signal on all pulse sequences with no enhancement or surrounding gliosis. A small Radiopaedia
Frequency and Location of Dilated Virchow-Robin
Large dVRS were detected in 33.2% of participants. Status cribrosum was found in 1.3% of participants. dVRS were also highly prevalent within the hippocampus (44.5%) and hypothalamus (11.6%). American Journal of Neuroradiology
Dilated Perivascular Spaces: Hallmarks of Mild Traumatic Brain
BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE: Recent animal and human studies have shown an increased frequency of enlarged, high-convexity Virchow-Robin spaces American Journal of Neuroradiology
Neuroimaging of Dilated Perivascular Spaces … – Wiley Online
Perivascular spaces (PVSs), also known as Virchow-Robin spaces, are pial-lined, fluid-filled structures found in characteristic locations throughout the brain. They Wiley Online Library
Brain Enlarged Perivascular Spaces as Imaging Biomarkers of …
ABSTRACT: Perivascular spaces or Virchow‐Robin spaces form pathways along the subarachnoid spaces that facilitate the effective clearance of brain metabolic AHA/ASA Journals
Enlarged Perivascular Spaces on MRI Are a Feature of
Enlarged perivascular spaces (EPVS), or Virchow-Robin spaces, are cerebrospinal fluid-filled cavities that surround small penetrating cerebral arterioles and correspond with extensions of the subarachnoid space. AHA/ASA Journals
See more new information: charoenmotorcycles.com
Perivascular Spaces \U0026 Its Mimics | Dr Utkarsh Kabra | Dnet
Perivascular Spaces
Ventricles And Cisterns Of The Brain | Radiology Anatomy Part 1 Prep | Mri Brain
Distended Perivascular Spaces In The Pons
Dilated Perivascular Spaces
Virchow Robin Spaces Chelushkin D. M.
Enlarged Perivascular Spaces In Brain Mri: Automated Quantification In Four Regions
Cisternostomy, Virchow Robin Space, Csf Shift Edema An How The Brains Cleans And Cools
Ct Of The Perirenal Space: Differential Diagnosis
Link to this article: dilated virchow robin spaces radiology.
See more articles in the same category here: https://charoenmotorcycles.com/how