What if the denominator is less than the numerator?
Numerator and Denominator in a Fraction Proper and improper fractions are the two sorts of fractions. A proper fraction is one in which the numerator is less than the denominator. An improper fraction is one in which the numerator is higher than the denominator.
What is a fraction whose denominator is greater than the numerator?
A fraction with denominator greater than the numerator is called a proper fraction. A fraction with numerator greater than the denominator is called an improper fraction.
What if the numerator is greater than the denominator, positive or negative?
When the numerator is greater than the denominator it is an improper fraction, such as 5/4. If both the numerator and denominator are positive numbers, or both are negative numbers, it will have a positive value always.
What is it called if numerator is less than denominator?
Proper fraction: The fraction whose numerator is always less than the denominator are called proper fractions. For Example: , etc. Thus, a fraction in which numerator is less than the denominator is called proper fraction.
What is a fraction whose numerator is smaller than its denominator?
A fraction in which numerator is less than the denominator is called proper fraction.
What is a fraction that has a numerator that is lower than the denominator?
Majorly, there are three types of fractions. Proper fractions: When the numerator of a fraction is less than its denominator, it is a proper fraction. This can also be described as a fraction less than 1 whole. For example, ⅙, ⅜, ⅘ are proper fractions.
What is the limit if the numerator is less than the denominator?
If the degree of numerator is less than that of the denominator then the limit is 0. If the degree of numerator is equal to that of the denominator then the limit is non-zero and equal to the ratio of leading coefficients of the numerator and denominator.
What is a proper fraction the numerator is less than the denominator?
Fractions that are less than one are known as proper fractions, and the numerator (the top number) is less than the denominator (the bottom number). A fraction with a numerator that is greater than or equal to the denominator is known as an improper fraction.
What fraction of a day is 8 hours?
Answer: 1/3rd of a day is 8 hours.
What if the numerator is greater than the denominator asymptote?
If the power fraction is an improper fraction-meaning the degree of the numerator is larger than the degree of the denominator, then there will be no horizontal asymptote. If the degree of the numerator is exactly one more that the degree of the denominator, then there is a slant asymptote.
What is an example of a numerator is greater than its denominator?
Improper fractions: When the numerator of a fraction is more than or equal to its denominator, it is called an improper fraction. For example, 4/3, 8/5, 6/4 are improper fractions.
What happens if the numerator is negative but the denominator is positive?
When the numerator and denominator have different signs, the quotient is negative.
When the numerator is greater than the denominator is positive or negative?
A viewer also explained how, in a fraction, if the numerator is bigger than the denominator, the result is a number bigger than one. In the reverse case, the number is less than one. The numerator or denominator do not determine whether the number is positive or negative.
Can the denominator be less than the numerator?
The denominator also indicates what kind of fraction it is. A proper fraction is one where the numerator is less than the denominator. An improper fraction is one where the numerator is greater than or equal to the denominator.
When the numerator is 2 less than its denominator?
If a numerator is 2 less than denominator of a rational number and when 1 is subtracted from numerator and denominator both, the rational number in its simplest form is 1/2.
What is a fraction with a smaller numerator than the denominator?
A proper fraction is a fraction whose numerator is smaller than its denominator. An improper fraction is a fraction whose numerator is equal to or greater than its denominator. 3/4, 2/11, and 7/19 are proper fractions, while 5/2, 8/5, and 12/11 are improper fractions.
What fraction of a day is 6 hours?
Answer: 6 hours is 1/4 of a day.
What is the lowest form of 30/40?
Therefore, 30/40 simplified to lowest terms is 3/4.
Which type of fractions has less numerators than denominators?
A fraction where the numerator is less than the denominator, then it is known as a proper fraction.
What fraction is whose numerator is greater than the denominator?
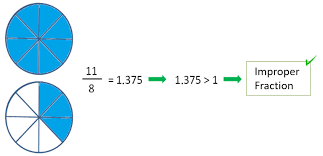
A fraction whose numerator is greater than its denominator is called an Improper fraction.
What if the numerator is greater than the denominator?
Answer: A fraction is called an improper fraction when the numerator is bigger than the denominator. The numerator indicates how many sections of the fraction are represented. It is placed in the upper part of the fraction.
What is a fraction whose numerator is less than its denominator called?
Proper fraction a fraction whose numerator is less than the denominator is called a proper fraction.
What to do if the numerator is smaller than the denominator?
A fraction with the numerator smaller than the denominator is called a proper fraction. For example, 1/4. And when you have a proper fraction, its decimal equivalent will be less than 1. For instance, 1/4 converted to a decimal would be 0.25.
What fraction of an hour is 50 minutes?
Answer: 1 hour = 60 minutes. So 50 minutes = 50/60 = 5/6 of an hour.
What happens if the degree of the numerator is smaller than the denominator?
The degree of the numerator is less than the degree of the denominator means that the horizontal asymptote will always be at y = 0. The degree of the numerator is greater than the degree of the denominator means that there is no horizontal asymptote.
What is the limit if the numerator is less than the denominator?
If the degree of numerator is less than that of the denominator then the limit is 0. If the degree of numerator is equal to that of the denominator then the limit is non-zero and equal to the ratio of leading coefficients of the numerator and denominator.
What is the remainder when the numerator is smaller than the denominator?
When the numerator is less than the denominator, the quotient is 0 with the remainder being whatever is left over. In this case, the entire numerator is left over because of the 0 quotient.
What is a proper fraction whose numerator is less than its denominator?
What happens if the numerator is less than the denominator?
What if the numerator is greater than the denominator?
What if the numerator and denominator are the same?
What are Proper Fractions?
Think of a pizza, okay? Let’s say it’s cut into eight slices. A proper fraction represents taking a part of that whole pizza, but you’re always taking *less* than the whole thing.
So, if you eat two slices, you’ve eaten 2/8 of the pizza. The 2 is the numerator (the top number), and it tells you how many slices you ate. The 8 is the denominator (the bottom number), and it tells you how many slices the whole pizza was cut into.
Key Features of Proper Fractions
Numerator less than Denominator: The most important thing about proper fractions is that the numerator is always smaller than the denominator. This means you’re representing a part of a whole, not the whole itself.
Value less than 1: Another cool thing about proper fractions is that their value is always less than 1. You can’t have more than the whole pizza, right? So, 2/8 is less than 1.
Representing Parts:Proper fractions are super useful for representing parts of things – think of a recipe where you need 1/4 cup of flour, or a map where you’re looking at a scale of 1/100.
Visualizing Proper Fractions
To really get it, let’s visualize it. Imagine a pie cut into four equal slices. If you eat one slice, you’ve eaten 1/4 of the pie. The slice represents the numerator, and the four slices in total represent the denominator.
Examples of Proper Fractions
Here are some examples of proper fractions:
1/2 (one half)
3/4 (three quarters)
2/5 (two fifths)
7/10 (seven tenths)
Why are Proper Fractions Important?
Proper fractions are like building blocks for understanding other types of fractions. Here’s why they’re so important:
Foundation for Other Fractions: They help us understand improper fractions (where the numerator is greater than or equal to the denominator) and mixed numbers (which combine a whole number and a proper fraction).
Real-World Applications: You encounter proper fractions in everyday life, like when you’re measuring ingredients, dividing objects, or dealing with proportions.
Calculations:Proper fractions are the foundation for many calculations, from adding and subtracting fractions to multiplying and dividing them.
Understanding Improper Fractions
Let’s go back to our pizza. If you eat five slices of an eight-slice pizza, you’ve eaten more than the whole pizza! That’s where improper fractions come in. You’d represent that as 5/8.
Mixed Numbers
A mixed number is a combination of a whole number and a proper fraction. If you ate the whole pizza (eight slices) and then two more slices, you’d have eaten 10 slices, or 10/8. This can also be expressed as a mixed number: 1 2/8.
Converting Improper Fractions to Mixed Numbers
To convert an improper fraction to a mixed number:
1. Divide the numerator by the denominator. In the example above, 10 divided by 8 equals 1 with a remainder of 2.
2. The whole number is the quotient. So, the whole number is 1.
3. The remainder becomes the numerator of the fraction. The remainder is 2.
4. The denominator stays the same. The denominator is still 8.
So, 10/8 becomes 1 2/8.
Converting Mixed Numbers to Improper Fractions
To convert a mixed number to an improper fraction:
1. Multiply the whole number by the denominator. In our example, 1 x 8 = 8.
2. Add the numerator to the product. 8 + 2 = 10.
3. Keep the same denominator. The denominator remains 8.
So, 1 2/8 becomes 10/8.
Simplifying Fractions
When you’re working with proper fractions (and other types of fractions), it’s often helpful to simplify them. This means finding the simplest form of the fraction, where the numerator and denominator have no common factors other than 1.
To simplify a fraction:
1. Find the greatest common factor (GCF) of the numerator and denominator. The GCF is the largest number that divides evenly into both numbers.
2. Divide both the numerator and denominator by the GCF.
For example, to simplify 2/4, the GCF of 2 and 4 is 2. Dividing both by 2, we get 1/2.
Adding and Subtracting Fractions
To add or subtract fractions with the same denominator:
1. Add or subtract the numerators.
2. Keep the denominator the same.
For example, 1/4 + 2/4 = 3/4.
To add or subtract fractions with different denominators:
1. Find the least common multiple (LCM) of the denominators. The LCM is the smallest number that both denominators divide evenly into.
2. Convert each fraction to an equivalent fraction with the LCM as the denominator.
3. Add or subtract the numerators.
4. Keep the LCM as the denominator.
Multiplying Fractions
To multiply fractions:
1. Multiply the numerators.
2. Multiply the denominators.
For example, 1/2 x 3/4 = 3/8.
Dividing Fractions
To divide fractions:
1. Flip the second fraction (the divisor).
2. Multiply the first fraction by the flipped fraction.
For example, 1/2 divided by 3/4 is the same as 1/2 multiplied by 4/3, which equals 4/6.
Real-World Examples of Proper Fractions
Cooking: A recipe might call for 1/2 cup of sugar or 1/4 teaspoon of salt.
Measurement: You might measure the length of a piece of fabric in yards or inches, using fractions like 1/2 yard or 3/4 inch.
Time: You might talk about 1/2 hour or 1/4 hour.
Probability: The chance of flipping a coin and getting heads is 1/2.
FAQs
Q: What is a fraction?
A: A fraction represents a part of a whole. It’s made up of a numerator (the top number) and a denominator (the bottom number). The numerator tells you how many parts you have, and the denominator tells you how many parts the whole is divided into.
Q: What is a proper fraction?
A: A proper fraction is a fraction where the numerator is smaller than the denominator. This means it represents a part of a whole, but not the whole itself.
Q: What is an improper fraction?
A: An improper fraction is a fraction where the numerator is greater than or equal to the denominator. This means it represents a whole or more than a whole.
Q: What is a mixed number?
A: A mixed number is a combination of a whole number and a proper fraction. It represents a value that is greater than 1 but less than 2, 3, or any other whole number.
Q: How do I convert a mixed number to an improper fraction?
A: To convert a mixed number to an improper fraction:
1. Multiply the whole number by the denominator.
2. Add the numerator to the product.
3. Keep the same denominator.
Q: How do I convert an improper fraction to a mixed number?
A: To convert an improper fraction to a mixed number:
1. Divide the numerator by the denominator.
2. The whole number is the quotient.
3. The remainder becomes the numerator of the fraction.
4. The denominator stays the same.
Q: How do I simplify a fraction?
A: To simplify a fraction:
1. Find the greatest common factor (GCF) of the numerator and denominator.
2. Divide both the numerator and denominator by the GCF.
Q: How do I add or subtract fractions?
A: To add or subtract fractions with the same denominator:
1. Add or subtract the numerators.
2. Keep the denominator the same.
To add or subtract fractions with different denominators:
1. Find the least common multiple (LCM) of the denominators.
2. Convert each fraction to an equivalent fraction with the LCM as the denominator.
3. Add or subtract the numerators.
4. Keep the LCM as the denominator.
Q: How do I multiply fractions?
A: To multiply fractions:
1. Multiply the numerators.
2. Multiply the denominators.
Q: How do I divide fractions?
A: To divide fractions:
1. Flip the second fraction (the divisor).
2. Multiply the first fraction by the flipped fraction.
Understanding proper fractions is crucial for working with all sorts of numbers. It’s the foundation for understanding other types of fractions, and it’s something you’ll use in tons of real-life situations.
See more here: What If The Denominator Is Less Than The Numerator? | A Fraction Whose Numerator Is Less Than The Denominator
A fraction in which numerator is less than the denominator is
The numerator of a fraction is 5 less than its denominator. If 3 is added to the numerator, and denominator both, the fraction becomes 2 3. Find the original fraction. BYJU’S
Proper Fraction – Definition, Difference, Examples
A fraction is called a proper fraction if its numerator is less than its denominator. The value of a proper fraction is always less than 1. Learn more about proper fractions with examples in this article. Cuemath
Proper Fractions – Math is Fun
So, a proper fraction is just a fraction where the numerator (the top number) is less than the denominator (the bottom number). Here are some examples of proper fractions: 1 2 Math is Fun
1.4: Fractions – Mathematics LibreTexts
Finding equivalent fractions where the numerator and denominator have no common factor other than \(1\) is called reducing to lowest terms. When learning how to reduce to lowest terms, it is helpful Mathematics LibreTexts
Numerator and Denominator: Definition, Difference
When the numerator of a fraction is greater than or equal to the denominator, it is called an improper fraction. Testbook
Numerator And Denominator – Math Steps, Examples
\cfrac {2} {3} \, 32 is a proper fraction because the numerator is less than the denominator. 2 < 3 2 < 3. Proper fractions are always less than one. An improper fraction is one in which the numerator is greater than the Third Space Learning
Understand fractions: FAQ (article) | Khan Academy
If a fraction is a whole then it means that the numerator (the top number) is equal to the denominator (the bottom number). If the numerator is more than the denominator, it Khan Academy
Fractions: Proper Fractions, Improper Fractions, and
A proper fraction is a fraction whose numerator is smaller than its denominator. An improper fraction is a fraction whose numerator is equal to or greater than its SparkNotes
See more new information: charoenmotorcycles.com
Proper Fraction A Fraction Whose Numerator Is Less Than The Denominator Is Called A Proper Fraction
How To Divide Fractions Where The Numerator Is Smaller Than The Denominator : Division Tips
Numerator Of A Fraction Is 4 Less Than Its Denominator. If 3 Added To Both…. Resulting 3/4
The Numerator Of A Fraction Is 4 Less Than The Denominator…|| Q. 1 Exercise 3.8 Rd Class 10 ||
Improper Fraction A Fraction Whose Numerator Is More Than Or Equal To The Denominator Is Calle
The Numerator Of A Fraction Is 4 Less Than The Denominator. If 1 Is Added To Both Its Numerator And
What Are Fractions? | Numerator, Denominator, And A Part Of A Whole
Rrb Po Clerk 2024 | Percentage In Maths For Bank Exam | Percentage Questions | Quant By Shubham Sir
Master The Art Of Comparing And Ordering Fractions Greater Than 1
Link to this article: a fraction whose numerator is less than the denominator.
See more articles in the same category here: https://charoenmotorcycles.com/how