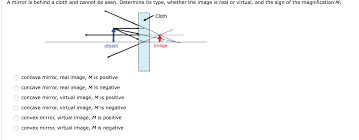
Can magnification of a concave mirror be positive?
A convex mirror’s magnification is always positive, but a concave mirror’s magnification can be either positive or negative. Based on the sign itself, this magnification can reveal information about the image’s nature. The picture is actual and inverted if the ratio is negative.
Is magnification of a concave lens positive or negative?
A concave lens always forms virtual, erect, and diminished image irrespective of the position of the object. Hence, the magnification is always is positive, but less than 1.
What is the magnification of a concave mirror?
may be less than or greater than one.
How magnification is positive in convex mirror?
As we have discussed in the above paragraph, the magnification of the virtual image is always positive, that is the magnification of a convex mirror is always positive and since the concave mirror forms both types of images, the magnification of the concave mirror can be both positive and negative.
Can magnification be negative convex?
(b) The magnification of the concave lens and convex mirror is always positive whereas the magnification of the convex lens and concave mirror can be positive or negative depending on the position of the object before the lens.
Can concave mirrors magnify?
Concave mirrors are used in various applications such as makeup application, shaving, flashlights, headlights, and telescopes due to their ability to form upright enlarged images, project parallel beams of light, and focus light for clearer and magnified images of distant objects.
Which one is not possible for the magnification by a concave mirror?
The magnification which is not possible for the concave mirror is M>-1. Explanation: The magnification in a concave mirror is determined by the height of the image to the height of the item.
Is magnification lens concave or convex?
An example of virtual images is the use of a magnifying glass. Magnifying glasses are convex lenses. When in use, the magnifying glass must be held close to the object being viewed so that the object is closer to the magnifying glass than its focal length.
Is magnification positive or negative for real image?
When the image formed is virtual and erect, magnification is positive. And, when the image formed is real and inverted, magnification is negative.
Do convex mirrors magnify?
A plane mirror always forms an image equal in size to the object, while a convex mirror always forms a diminished image. Only a concave mirror can form a magnified image. So, the correct choice is (c). Q.
What is the expression for magnification for concave mirror?
Hence, the expression for magnification (m) becomes: m = h’/h = -v/u. Q.
What does the magnification of a concave mirror is 1.75 mean?
Explanation: A magnification of 1.75 means that the image formed by the concave mirror is 1.75 times larger than the object. In other words, the image is almost twice as big as the object. This also tells us that the concave mirror is producing a magnified image of the object.
Is the magnification of a concave lens always positive or negative?
The concave lens and the convex mirror always produce a virtual image, therefore, their magnification is always positive whereas the convex lens and the concave mirror can produce real as well as the virtual image depending upon the object position, therefore, their magnification can be positive or negative.
Is the power of a concave mirror positive or negative?
So, power for a concave mirror is negative. Note: Students should always read whose power is asked by the lens or mirror. The focal length of a concave surface is negative, whereas the focal length of a convex surface is positive.
Is convex mirror positive or negative?
(c) Image distances (v) for a convex mirror is always positive because the image is always formed behind the mirror.
Can magnification of a concave mirror be negative?
A concave mirror has negative magnification. The height of the image divided by the height of the object determines the magnification of the concave mirror. Therefore, if the image is inverted and real then the magnification will be negative.
What if magnification is positive in a concave mirror?
Magnification produced by a concave mirror is positive, when the image is virtual and erect.
Why does a convex mirror have positive magnification?
Flexi Says: The image formed by a convex mirror is always virtual and upright. Hence, the magnification produced will always be positive and <1.
What is the magnification of concave mirrors?
In a concave mirror, when the distance of the object is less than the focal length, the magnification will be greater than one. When the distance of the object is greater than the focal length, then the magnification is less than one.
Does convex or concave magnify?
Using a convex lens on your eye will correct the problem. This works because the convex lenses curve the ray of right correctly onto your retina, allowing the focal point to be shorter. A convex lens is always used in a microscope because of its ability to magnify images.
Do concave mirrors enlarge?
Concave mirrors can produce both real and virtual images; they can be upright (if virtual) or inverted (if real); they can be behind the mirror (if virtual) or in front of the mirror (if real); they can also be enlarged, reduced, or the same size as object. 2.
Can concave mirrors have zero magnification?
Manification cannot be zero as m = -v/u = I/o. In the special case, say for convex lens when u = ∞, then v = f and M = −f / ∞ = 0.
Are convex mirrors always magnified?
For a real object ( that is object placed anywhere on the reflecting side of a convex mirror ) a virtual, erect and diminished image is formed. Only when a virtual object ( that is object placed on the silvered side ) is placed in between the pole and focus of a convex mirror, we get a real ,erect and enlarged image.
Why concave mirror is not used in magnifying glass?
Complete answer: We can observe that in a concave lens, the light beam coming from the source diverges, so the image formed will be virtual and diminished. Therefore, a concave lens cannot be used as magnifying glass.
Is the magnification of a concave lens always negative?
(b) The magnification of concave lens and convex mirror is always positive where as the magnification of convex lens and concave mirror can be positive or negative depending on the position of the object before the lens.
Are magnifying mirrors concave?
The level of magnification is caused by the concave shape of the mirror. The concave shape of the mirror concentrates the light beams, intensifying the light beams as it gets closer to the focal point therefore providing you with the close up magnified views.
What is the difference between magnification of convex and concave mirror?
Reason: Magnification of a convex mirror is always positive, but that of a concave mirror may be both positive or negative.
What does it mean when the magnification of a mirror is negative?
An inverted image is always real for a mirror and a lens. Therefore, a negative magnification further indicates that the image is real and inverted.
What does it mean if magnification is positive?
If the magnification is positive, the image is upright compared to the object; if m is negative, the image is inverted compared to the object.
Which one is not possible for the magnification by a concave mirror?
The magnification which is not possible for the concave mirror is M>-1. Explanation: The magnification in a concave mirror is determined by the height of the image to the height of the item.
What does magnification +3 mean?
Explanation: Given, the required magnification is +3. So, the image is needed to be straight and virtual and 3 times magnified.
How do you know if a mirror is a concave or convex?
What is the magnification of a concave mirror?
Do concave mirrors have a positive focal length?
How does a concave mirror create a real image?
Concave Mirrors: A Quick Refresher
Before we get into the nitty-gritty of magnification, let’s remember what a concave mirror is. It’s like a spoon, you know? The inner surface is reflective. Think about it this way:
Concave mirrors curve inwards, like a cave.
Convex mirrors curve outwards, like the outside of a bowl.
Concave mirrors are all about convergence. They gather light rays and focus them at a single point, which we call the focal point. This is where the magic of magnification happens.
Magnification: The Bigger Picture
Magnification is essentially how much bigger or smaller an image appears compared to the actual object.
Positive magnification means the image is upright and enlarged.
Negative magnification means the image is inverted and reduced in size.
The Math Behind Magnification
To calculate magnification (m) for a concave mirror, we use a simple formula:
m = – (v/u)
Where:
v is the image distance, the distance between the mirror and the image.
u is the object distance, the distance between the mirror and the object.
Let’s break down this formula to understand why we get a positive or negative magnification.
Positive Magnification: The “Enlarging” Effect
Imagine you’re holding a flower in front of a concave mirror. If you place the flower closer to the mirror than its focal point (u < f), you'll see a virtual, upright, and magnified image. This means the image is behind the mirror, and it's bigger than the actual flower! This is where the positive magnification comes into play. Since the image distance (v) is behind the mirror, it's considered negative. But because you're dividing a negative (v) by a negative (u), the result is positive. Positive magnification = Enlarged, upright image. Negative Magnification: The "Shrinking" Effect Now, let's move the flower further away from the concave mirror, beyond its focal point (u > f). This time, the image will be real, inverted, and smaller than the actual flower. It’s located in front of the mirror, which means the image distance (v) is positive.
Since you’re dividing a positive (v) by a negative (u), the result is negative.
Negative magnification = Reduced, inverted image.
So, When is Magnification Positive and When is it Negative?
Here’s a simple breakdown:
Positive Magnification:
* Object is closer to the mirror than the focal point (u < f)
* Image is virtual, upright, and enlarged
* Image is behind the mirror (v is negative)
Negative Magnification:
* Object is further away from the mirror than the focal point (u > f)
* Image is real, inverted, and reduced
* Image is in front of the mirror (v is positive)
FAQ: Answering Your Burning Questions
Q: What happens when the object is at the focal point (u = f)?
A: When the object is at the focal point, the light rays from the object become parallel after reflection. This means the image is formed at infinity. In this case, the magnification is infinite because the image distance becomes infinitely large.
Q: Is the magnification always the same for a specific concave mirror?
A: No! Magnification depends on the object’s distance from the mirror. The closer the object, the greater the magnification.
Q: Can a concave mirror produce a real image that’s larger than the object?
A: Absolutely! This happens when the object is between the center of curvature and the focal point (f < u < 2f). Q: Can a concave mirror produce a real image that's smaller than the object? A: Yes, this happens when the object is beyond the center of curvature (u > 2f).
Q: What’s the difference between a real image and a virtual image?
A: A real image is formed by the actual convergence of light rays, and it can be projected onto a screen. A virtual image is formed by the apparent intersection of reflected or refracted rays, and it cannot be projected onto a screen.
Q: How can I tell if a concave mirror is being used to magnify or shrink an object?
A: Look at the image formed by the mirror. If the image is larger than the object, the mirror is magnifying. If the image is smaller than the object, the mirror is shrinking it.
Q: Why is magnification negative for a concave mirror?
A: The negative sign in the magnification formula indicates that the image is inverted. It’s a convention to represent inverted images with a negative sign.
Q: How do I use magnification to understand the behavior of light in a concave mirror?
A: Magnification helps you visualize how the mirror affects the size and orientation of the image. It’s a valuable tool for understanding the principles of reflection and how light interacts with curved surfaces.
In Conclusion
Understanding the concept of magnification for concave mirrors is crucial for comprehending their behavior. Remember, the sign of magnification tells you if the image is upright or inverted, and its magnitude tells you how much bigger or smaller the image is compared to the object.
See more here: Is Magnification Of A Concave Lens Positive Or Negative? | Magnification Of Concave Mirror Is Positive Or Negative
Give me the sign convention in concave and convex mirrors
Q. Assertion :Magnification of a convex mirror is always positive, but that of a concave mirror may be both positive or negative. Reason: It depends on the sign convention chosen. BYJU’S
Physics Tutorial: Image Characteristics for Concave Mirrors
Concave mirrors can produce both real and virtual images; they can be upright (if virtual) or inverted (if real); they can be behind the mirror (if virtual) or in front of the mirror (if real); they can also be enlarged, The Physics Classroom
2.3: Spherical Mirrors – Physics LibreTexts
The focal length \(f\) is positive for concave mirrors and negative for convex mirrors. The image distance \(d_i\) is positive for real images and negative for Physics LibreTexts
Magnification for a concave mirror – Physics Stack
concave mirrors have positive $f$ and convex mirrors have negative $f$. for magnification, positive values indicate that the image is the same orientation as the Physics Stack Exchange
25.7 Image Formation by Mirrors – College Physics 2e – OpenStax
What happens if an object is closer to a concave mirror than its focal length? This is analogous to a case 2 image for lenses ( d o < f d o < f and f f positive), which is a OpenStax
How to Calculate the Magnification of a Concave Mirror
If the magnification is positive, then the image is virtual and if the magnification is negative, then the image is real. We will use these steps, definitions, and equations to calculate Study.com
Physics Tutorial: The Mirror Equation – Convex Mirrors
To obtain this type of numerical information, it is necessary to use the Mirror Equation and the Magnification Equation. The mirror equation expresses the quantitative relationship The Physics Classroom
Spherical mirrors; and Refraction – Boston University
To figure out what the signs mean, take the side of the mirror where the object is to be the positive side. Any distances measured on that side are positive. Distances measured on the other side are negative. f, the Boston University Physics Department
See more new information: charoenmotorcycles.com
Mirror Formula And Magnification | Sign Convention
Concave Mirrors And Convex Mirrors Ray Diagram – Equations / Formulas \U0026 Practice Problems
Magnification Of Image Size In Spherical ( Convex And Concave ) Mirrors
Image Distance And Image Height: Mirror Equation And Magnification Equation
Magnification Equation For Mirrors
Magnification Of Mirror//Concave Mirror
Mirror Formula And Magnification
10 Mirror Formula And Magnification
Concave Mirror Demo: Pendulum
Link to this article: magnification of concave mirror is positive or negative.
See more articles in the same category here: https://charoenmotorcycles.com/how