What is the method for isolation of Trichoderma?
Method for isolation of Trichoderma Soil samples are collected, air dried, and ground into powder. Stock solution of sample is prepared by dissolving 10 g of powdered soil sample into 90 mL of distilled water. Next, serial dilution of samples were prepared as 10−1, 10−2… 10−5.
Which media is used for isolation of Trichoderma?
From all the media evaluated, PDAm was the most effective in the isolation of Trichoderma spp. and Gliocladium spp. (2.16 and 1.53 CFU, respectively); being lower in PDA (1.70 and 1.32 CFU, respectively). In Martin medium, the colony abundance of Trichoderma spp.
How to apply Trichoderma to soil?
Cutting and seedling root dip: Mix 10g of Trichoderma powder along with 100g of well rotten FYM per litre of water and dip the cuttings and seedlings for 10 minutes before planting. 4. Soil treatment: Apply 5 Kg of Trichoderma powder per hectar after turning of sun hemp or dhaincha into the soil for green manuring.
What is the method of production of Trichoderma?
Molasses yeast medium is prepared as detailed below. The medium is prepared and dispensed into conical flasks and sterilized at 15 lb pressure for 15 minutes in an autoclave. After the medium is cooled it is in inoculated with 10 days old fungal disc of T. viride and then incubated for 10 days for fungal growth.
How do you get rid of Trichoderma in soil?
Unfortunately, Trichoderma is tough to get rid of once it starts growing. It’s resistant to most chemicals and pesticides. However, picking the affected mushrooms and immersing them in water heated to 140 °F (60 °C) seems to work. Keep the mushrooms in the water for 30 minutes to kill any mold spores.
What are the methods of isolation of fungi from soil?
Techniques used for isolation of fungi from soil include serial dilution agar plate, Warcup soil plate, syringe inoculation, immersion tube method, screened immersion plates, plate profile, hyphal isolation, soil washing, partial presterlization, soil sieving, floatation, baiting etc.
What culture medium for Trichoderma?
Potato Dextrose Agar was the best medium in terms of growth spore production and biomass yield.
Which media is commonly used for isolation of fungi?
Selective media, like Inhibitory mould agar and Dermatophyte test media are important in the isolation of fungal pathogens such as Cryptococcus neoformans and dermatophytes [4].
What media is best for fungi isolation?
20.2.2 Media for isolating fungal endosymbiont For isolating endophytic fungi, some of the important media are malt extract media, (PDA) potato dextrose agar, mycological agar (MCA) and malt yeast extract agar (MYA).
How do you make Trichoderma selective media?
Trichoderma harzianum Selective Agar Base is recommended for selective isolation of Trichoderma harzianum . Suspend 25.54 grams(the equivalent weight of dehydrated medium per litre) in 960 ml distilled water. Heat to boiling to dissolve the medium completely.
What is the best temperature for Trichoderma?
Trichoderma harzianum is the most commonly known species of this beneficial fungi. It likes to hang out in temperatures between 86 to 98.6 degrees Fahrenheit. It is used as a fungicide and a biocontrol for several different fungal pathogens.
At what pH does Trichoderma grow?
The most favorable pH ranges between 5.5 and 7.5 in which total dry weight of mycelium varies between 1.41 and 1.35 g.
How to multiply Trichoderma?
It has benefits as a plant growth promoter and biocontrol agent. Trichoderma can be mass multiplied using rice or other grains in a pressure cooker. It is formulated and applied to seeds, soil, and other plant parts.
How do you get Trichoderma?
To infest a mushroom crop, Trichoderma first must have its spores introduced. The spores can adhere themselves to employees and their clothing, as well as to equipment and plastic surfaces around a mushroom farm, flies or on mites. Spores must exist in sufficient numbers and correct conditions must prevail.
What is Trichoderma isolated from?
A total of 1308 Trichoderma strains were obtained by the dilution plate method and single spore isolation method, including 1018 strains from 1018 rhizosphere soil samples, 205 strains from 45 rotten wood samples, and 86 strains from 16 plant samples.
What chemical kills Trichoderma?
Phenolic disinfectants are the most suppressive to the growth of Trichoderma mycelium, and of these, Disolite is more effective in killing Trichoderma spores than Environ or Prophyl at the same dilution rate.
What are the protocols for isolation of fungi?
– If septate hyphae are observed, cut/mince tissue into smaller pieces to increase the chance of isolation of the fungi. Inoculate the homogenate as well as the small pieces of minced tissue on appropriate agar plates (1x BHIA plate, 2x SDA plates and 1x SDA plate containing cycloheximide and chloramphenicol).
What is the direct method of isolation of fungi?
Sabouraud dextrose agar (SDA) is used to isolate and cultivate fungi and yeasts from clinical specimens. It contains nutrients like dextrose and enzymatic digest of casein to support fungal growth, and antibiotics to inhibit bacteria.
How do you isolate mycorrhizal fungi from soil?
Monitoring the dynamics of the spore bank of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi (AMF) is essential for the sustainable management and protection of agroecosystems. The most common method for extracting AMF spores from soil is the wet-sieving technique (WST).
How do you prepare Trichoderma culture?
The preparation method of trichoderma is characterized by comprising the following steps: smashing a carrier, controlling fineness of the carrier to be 40-60 meshes, adjusting the humidity to be 8-12%, adding an ultraviolet protective agent into the carrier, and evenly mixing for reservation; and performing normal- …
How to isolate Trichoderma harzianum?
Disease-free plant parts stem, root, and leaves were separated with a sterile scalpel and stored in sterile plastic bags at 4 °C until transported to the laboratory to isolate the endophytic fungi.
What is the liquid medium for Trichoderma?
The medium that is suitable for the large scale culture of Trichoderma spp. conidia is a liquid basal medium that contains potato dextrose broth as a carbon source. The medium also contains an additional carbon source and a nitrogen source.
How to isolate fungi from soil?
Soil fungi were isolated by using dilution plating technique and was identified by Biolog’s Microbial Systems.
What is the best medium for fungi isolation?
4.3. Soil has been primarily used as the source to isolate fungi (Mothapo et al., 2015), although some other sources (e.g., woodchips collected from a denitrifying bioreactor) were also used (Aldossari and Ishii, 2021).
What agar is used for fungi isolation?
Waksman routinely used an agar medium composed of dextrose, peptone, KrLjPO^ and MgSO^^O for the isolation of soil fungi. This medium was acidified to pH 4.0 to prevent or reduce the growth of bacteria.
Which method is most preferable in isolation of fungi?
They compared different isolation techniques and found that the “mortar and pestle isolation method” was the most effective when comparing the number of morphotypes.
What is the direct method of isolation of fungi?
Sabouraud dextrose agar (SDA) is used to isolate and cultivate fungi and yeasts from clinical specimens. It contains nutrients like dextrose and enzymatic digest of casein to support fungal growth, and antibiotics to inhibit bacteria.
How do you isolate Entomopathogenic fungus?
Entomopathogenic fungi for exploitation purposes for formulations of biological products can be isolated directly from insect corpses or from soil samples collected in natural areas since a considerable part of their lives act as saprophytes in soils (Sharma et al.
How do you preserve Trichoderma?
Drying method proved to be best for the preservation of Trichoderma viride for long period of time. It is an easy, convenient, economical, and effective tool for the preservation of Trichoderma viride isolate.
How to isolate Trichoderma spp from different sources?
Which species of Trichoderma were isolated from the soil?
How effective are Trichoderma isolates against plant pathogenic fungi?
How do you biocontrol Trichoderma?
You know, isolating Trichoderma from soil is a pretty common practice, especially if you’re into the world of biocontrol or mycology. These fungi are a real powerhouse, known for their ability to fight off harmful pathogens, promote plant growth, and even boost soil health. But, before you can harness their amazing power, you gotta get your hands on them first. So, let’s dive into the nitty-gritty details of isolating Trichoderma from soil.
Gear Up!
First things first, you’ll need the right tools for the job. Here’s what you’ll need:
Soil Sample: You’ll need a good sample of soil from an area where you suspect Trichoderma might be lurking. Think about places with good organic matter, like gardens or compost piles.
Sterile Water: You’ll need this to dilute your soil sample and make it easier to work with.
Petri Dishes: These are your trusty companions for growing your Trichoderma colonies.
Potato Dextrose Agar (PDA): This is a common growth medium for fungi, and it’s perfect for encouraging your Trichoderma to grow and thrive.
Incubator: This is where you’ll nurture your Trichoderma colonies, providing them with the ideal temperature and humidity.
Microscope: This is your secret weapon for identifying your Trichoderma colonies.
Sterile Pipettes: These are handy for transferring your soil dilutions and inoculating your PDA plates.
Bunsen Burner & Sterilizing Equipment: Keeping things sterile is crucial, so you’ll need a Bunsen burner and sterilizing equipment to keep those pesky contaminations at bay.
Gloves and Mask: Protecting yourself from anything lurking in the soil is a good idea, so don’t forget to wear gloves and a mask.
The Isolation Process: A Step-by-Step Guide
Now, let’s break down the isolation process step by step:
1. Sample Collection: Grab your soil sample, but make sure it’s representative of the area you’re interested in. You don’t want to just grab a handful from the surface – go a little deeper!
2. Soil Dilution: Take a small amount of your soil sample and mix it with sterile water in a sterile container. The goal is to create a suspension with a good concentration of Trichoderma spores. Think of it as making a “fungal smoothie” – not too thick, not too thin!
3. Plate Inoculation: Time to get those PDA plates ready! Use your sterile pipettes to transfer a few drops of your soil suspension onto each PDA plate. This is like planting the seeds of your Trichoderma colonies.
4. Incubation: Now, let the magic happen! Pop those PDA plates into your incubator, set the temperature to around 25°C (77°F), and let them hang out for a few days. You’ll soon see little colonies of Trichoderma start to emerge.
5. Colony Selection: Once your Trichoderma colonies have grown, you need to select the ones that are healthy and isolated. Look for colonies that are distinctive in color, texture, or growth patterns, and avoid any that look contaminated.
6. Subculturing: You’ll need to transfer your selected Trichoderma colonies to new PDA plates to create pure cultures. This involves carefully removing a small portion of the colony with a sterile tool and transferring it to a fresh plate. Think of it as giving your Trichoderma a new home!
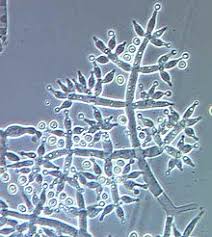
7. Microscopic Identification: Under your microscope, Trichoderma will reveal its unique features – look for branching hyphae and conidia. You might need a fungal identification guide to confirm your findings.
Tips & Tricks
The Art of Sterility: This is crucial! Make sure you’re working in a sterile environment to avoid contamination. Keep your workspace clean, use sterile tools and supplies, and practice good lab hygiene.
Don’t Give Up: Sometimes, isolating Trichoderma can take a few attempts. If your first try doesn’t yield good results, don’t be discouraged! Just keep experimenting with different soil samples and techniques.
Embrace the Variability: Just like us, Trichoderma comes in different forms, each with its unique qualities. Don’t be afraid to explore different strains and see which ones work best for your needs.
Applications of Trichoderma
Now that you’ve successfully isolated your Trichoderma treasure, what can you do with it? The possibilities are endless! Here are just a few examples:
Biocontrol Agent: Trichoderma can be a natural weapon against plant pathogens, helping to protect crops from disease.
Plant Growth Promoter: Trichoderma can boost plant growth by enhancing nutrient uptake and promoting root development.
Soil Health Enhancer: Trichoderma can improve soil structure and fertility by breaking down organic matter and making nutrients more available.
Bioremediation: Trichoderma can even be used to clean up contaminated soil and water.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What’s the best type of soil to collect for isolating Trichoderma?
You’ll have the best luck with soil samples that are rich in organic matter, like garden soil, compost piles, or soil from around healthy plants.
How long does it take to isolate Trichoderma?
The time it takes depends on the growth rate of the Trichoderma strains you’re isolating. It can take anywhere from a few days to a couple of weeks.
What are the key features of Trichoderma colonies that I should look for?
Trichoderma colonies often exhibit features like rapid growth, velvety or powdery texture, and distinctive colors, such as green, white, or yellow. They also tend to have a unique branching, thread-like structure that distinguishes them from other fungi.
How can I store my isolated Trichoderma for future use?
You can store your Trichoderma cultures on PDA plates, in a refrigerator at 4°C (39°F), or even by freeze-drying them. Just make sure to label them clearly and store them in a way that prevents contamination.
Is it safe to work with Trichoderma?
Trichoderma is generally considered safe for humans, but it’s always a good idea to wear gloves and a mask when working with it, especially with the original soil sample.
Where can I find more information about Trichoderma isolation and applications?
There are lots of resources available! Check out scientific journals, online databases, university websites, and specialized mycology forums.
I hope this guide helps you on your journey to isolating Trichoderma. Remember, it’s all about patience, practice, and a good dose of fungal enthusiasm. So, get out there, get your hands dirty, and unlock the amazing world of Trichoderma!
See more here: Which Media Is Used For Isolation Of Trichoderma? | Isolation Of Trichoderma From Soil
Isolation of Trichoderma spp. from various types of soil and its …
Trichoderma is a free-living fungus having high potential for soil born disease management in plants which are commonly found in soil and root ecosystem. It has a tendency to increase the growth… ResearchGate
Introductory Chapter: Identification and Isolation of
Trichoderma spp. is one of the frequently isolated fungal genera from soil and plant roots that have been extensively studied for IntechOpen
Isolation of Trichoderma in the rhizosphere soil of Syringa oblata
Thirty-three Trichoderma species were isolated from 150 rhizosphere soil samples of chili (Nawaz et al., 2018). Trichoderma has been worldwidely researched for ScienceDirect
(PDF) Isolation, Characterization, Cultivation of
Trichoderma is a genus of anamorphic fungi that are mostly found in rhizospere soil. and can be used to combat fungal phytopathogens (Fusarium spp which cause the wilt stem in chilli plant). ResearchGate
Isolation and Mass Production of Trichoderma | SpringerLink
The first step in any successful Trichoderma biocontrol research program is the isolation of candidates and typically this is achieved by either bioprospecting Springer
The Isolation and Characterization of Antagonist
The soil dilution plate method was used to isolate Trichoderma (Trichoderma Specific Medium (TSM)). Isolated Trichoderma were evaluated for their antagonistic potential against Fusarium MDPI
doi: 10.1007/978-1-0716-1724-3 17 – Springer
Trichoderma can be isolated from soil, water, plant root, and decaying plant. Trichoderma plays key role in biocontrol of plant pathogens, plant growth promotion, Springer
Chapter Introductory Chapter: Identification and Isolation
ive isolation of Trichoderma spp. from soil. It is composed of low glucose level for rapid growth and sporulation of the fungus. Chloramphenicol is used to inhibit the growth of intechopen.com
Isolation and molecular identification of Trichoderma species from …
Herein, we isolated a total of 18 Trichoderma strains divided to nine species such as T. atroviride, T. virens, T. velutinum, T. harzianum, T. asperellum, T. ScienceDirect
See more new information: charoenmotorcycles.com
How To Isolate Trichoderma From Soil?
Trichoderma Mold Fungi Timelapse
Isolation And Estimation Of Soil Borne Pathogens By Serial Dilution Method
Isolation Of Fungi From Soil Sample | Fungal Isolation Technique
Trichoderma Viride… Inoculation Into Potato Dextrose Broth For Mass Multiplication
Trichoderma Production
How To Culture Tricoderma At Home
Ủ Phân Bằng Hệ Thống Asp Phần 2: Nhân Sinh Khối Nấm Trichoderma Phiên Bản Vô Hạn.
Cách Ủ Phân Hữu Cơ Đơn Giản Với Trichoderma
Cara Mudah Mendapatkan Isolat Trichoderma Dan Gliocadium
Link to this article: isolation of trichoderma from soil.
See more articles in the same category here: https://charoenmotorcycles.com/how/