What does the ovule of a flower develop into?
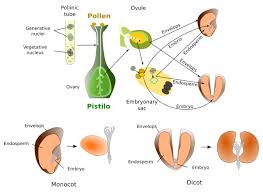
The ovule plays a crucial role in flower reproduction. It is the organ within the plant that produces and houses egg cells. After fertilization, the ovule becomes the fruit, seed, or seeds of the plant. The ovule consists of an integument and a nucleus located within the ovary of flowering plants.
What do the integuments in a flower develop into the _____ in a fruit?
(The integuments of the ovule develop into the seed coat, which gives rise to the seed, and the ovary develops into a fruit.)
What does the ovary develop into?
The ovary contains ovules, which develop into seeds upon fertilization. The ovary itself will mature into a fruit, either dry or fleshy, enclosing the seeds.
What do ovules change into?
After fertilisation, the ovule is converted into seed and ovary into fruit.
What does each ovule develop into?
Final answer: After fertilization, the ovule develops into the seeds.
What is the integument of the ovule?
An integument is a protective layer of cells surrounding the ovule. Gymnosperms typically have one integument (unitegmic) while angiosperms typically have two integuments (bitegmic).
What do integuments develop into?
The ovular integuments develop into seed coats. The outer seed coat is called the testa and the inner coat is called the tegmen.
What is integument in flowering plants?
An integument is a protective cell layer surrounding the ovule. Gymnosperms typically have one integument (unitegmic) while angiosperms typically have two (bitegmic).
What do the integuments of the ovule become upon maturation of a fruit?
The integuments of the ovule become the seedcoat of the mature seed. This sometimes consists of two distinct coverings, a typically firm outer seedcoat, the testa, and a generally thin, membranous inner coat, the tegmen.
Where does the ovary develop in a flower?
In the flowering plants, an ovary is a part of the female reproductive organ of the flower or gynoecium. Specifically, it is the part of the pistil which holds the ovule(s) and is located above or below or at the point of connection with the base of the petals and sepals.
What starts to develop in the ovary?
Follicular development starts in the core of the ovary, where these primordial follicles become primary follicles (primary oocyte surrounded by a single layer of cuboidal granulosa cells) and secondary follicles (primary oocyte surrounded by more than one layer of cuboidal granulosa cells).
What does the ovary of the flower develop into a dash?
The ovary of a flower develops into a fruit after pollination.
What do the ovules in a flower develop to form?
After fertilisation, the ovary of a flower begins to grow and develops into a fruit. Hence, a fruit is a mature or ripened ovary. The ovules inside the ovary develop into seeds. A fruit encloses the seeds inside.
What is a woman’s egg made of?
The ovum itself has a central nucleus that contains the female’s genetic material; this, with the genetic material in the sperm cell, determines the inherited characteristics of the child. Surrounding the nucleus is a cell plasma, or yolk, that contains nutritional elements essential to the developing egg cell.
Is ovule male or female?
The style leads to the ovary that contains the female egg cells called ovules. The male parts are called stamens and usually surround the pistil.
What does the ovule in a plant develop into?
ovule, plant structure that develops into a seed when fertilized. A mature ovule consists of a food tissue covered by one or two future seed coats, known as integuments.
What does ovule turn to?
After fertilisation the fertilised egg develops into an embryo and the primary endosperm nucleus into the endosperm. The ovule is converted into seed and ovary into fruit.
What does a fully developed ovule become?
In flowering plants after fertilisation, the zygote develops into the embryo, the ovules develop into the seed and the ovary develops into the fruit. Also, the sepals, petals and stamens of the flower generally fall off.
What does the integument develop into?
2.1 Terminology applied to integument layers- In the bitegmic ovules of angiosperms, it is suggested that the inner integument will develop into the tegmen and the outer integument will form the testa, hence, the tegmen and testa form the seed coat (Corner, 1976).
What does ovule integument get transferred into?
Ovule integuments gets transformed into seed coat. Outer integument becomes testa and inner integument becomes tegmen.
What does the integument inside the ovary become?
Integument is a protective envelope covering the ovule. After the process of fertilization, the integuments gets transformed to form the seed coat. If there are two integuments the condition is known as bitegmic. In such a case the seed will have two seed coats.
What are the integuments of the ovule?
The outer layer of the ovule is known as the integument. They are two integuments, inner integument, and outer integument. There is a small opening in Integuments, referred to as Micropyle. The micropyle is referred to as the top end of the ovule.
What is the ovule development of a plant?
Ovule First and foremost, the ovule is a structure found in plants that develops into a seed during the process of reproduction. When it is mature, it contains food tissue, and one or two future seed coats cover it, which we refer to as integuments.
What do ovary develop into?
The ovary, which once contained the ovule, often transforms into a fleshy fruit. The fruit contains the newly formed seed and, therefore, the developing embryo. Fruit is a tasty, often sugary incentive to animals, who can eat the fleshy fruit and then deposit any undigested seeds within it elsewhere in their feces.
Why do the integuments of an ovule harden?
Integuments of ovule harden to form tough protective seed coats. The micropyle remains as a smal pore in the seed coat. This facilitates is entry of oxygen and water into the seed during germination.
What does the integument produce?
The integumentary system comprises the skin, hair, nails, and glands that produce sweat and oil. It is a complex organ that helps protect the body and regulates various essential processes. These tissues work together to protect the body from infection and injury and regulate bodily processes.
What is the function of the ovule in a flower?
The ovule is the organ that forms the seeds of flowering plants. It is borne in the ovary of the flower and consists of nucellus protected by integuments, precursors of embryo/endosperm, and seed coat, respectively.
Does ovule develop into a seed?
In flowering plants after fertilisation, the zygote develops into the embryo, the ovules develop into the seed and the ovary develops into the fruit. Also, the sepals, petals and stamens of the flower generally fall off.
What develops into a fruit and the __________ develops into a seed?
After fertilisation, the ovary of a flower begins to grow and develops into a fruit. Hence, a fruit is a mature or ripened ovary. The ovules inside the ovary develop into seeds.
What does the ovule present in an ovary grows to become?
After fertilization the ovary develops into fruit while ovules develop into seeds.
What do a flower, ovule, and ovary become quizlet?
The ovary develops into fruit. Located in the ovary. The ovule contains an egg which developes into a seed after it is fertilized.
What is a ovule in a plant?
Which part of the ovule is made up of integuments?
What is integument in a plant?
What is a seed ovule?
The Journey of an Ovule
You know that ovules are the structures that eventually become seeds in flowering plants. They’re nestled within the ovary of a flower. And guess what? The integuments, which are layers of protective tissue, play a crucial role in this whole seed-making process.
Think of the integuments like a protective shell for the ovule. They’re kind of like the outer layers of a nut that safeguard the precious kernel inside.
What Happens to the Integuments?
Now, let’s get to the heart of your question. In flowering plants, the integuments undergo a remarkable transformation. As the ovule develops, the integuments grow and envelop the megasporangium (which contains the megaspore that will ultimately develop into the female gametophyte).
The integuments eventually fuse together, leaving a small opening called the micropyle. This opening is super important because it’s the pathway through which the pollen tube will eventually travel to deliver the sperm to the egg cell within the ovule.
But the most interesting thing is what happens after fertilization. You see, after the sperm from the pollen tube fertilizes the egg cell, the integuments don’t just sit there. They start transforming into a tough, protective seed coat.
From Integuments to Seed Coat: The Transformation
The seed coat, formed from the integuments, has several vital functions:
Protection: It acts as a shield for the developing embryo and the endosperm, safeguarding them from environmental stress, drying out, and potential damage from insects or other organisms.
Dormancy: The seed coat can also help regulate dormancy. This means it can keep the seed from germinating until conditions are favorable for growth.
Dispersal: In some plants, the seed coat has features that help with seed dispersal, like wings, hooks, or fleshy coverings that attract animals to eat them and spread the seeds elsewhere.
So, basically, the integuments start as protective layers and then morph into the tough, resilient seed coat that wraps around the embryo and endosperm.
The Integuments and Seed Development
This transformation from integuments to seed coat is a fascinating process that’s essential for the successful development of seeds in flowering plants. Understanding how this happens helps us appreciate the complex and intricate nature of plant reproduction.
And remember, the seed coat isn’t just a passive outer layer. It plays a critical role in protecting the next generation of plants and ensuring their survival.
FAQs
1. What exactly are integuments?
Integuments are layers of protective tissue that enclose the megasporangium within an ovule. Think of them like the protective shell around a nut.
2. What’s the difference between integuments and a seed coat?
While integuments are the initial protective layers of the ovule, the seed coat is the tough, protective outer layer of the seed that develops from the integuments after fertilization.
3. How does the micropyle form?
The micropyle forms when the integuments fuse together, leaving a small opening. This opening allows the pollen tube to reach the egg cell for fertilization.
4. Why are seed coats important?
Seed coats are essential for protecting the developing embryo and endosperm, ensuring their survival, regulating dormancy, and sometimes even helping with seed dispersal.
5. Do all flowering plants have seed coats?
Yes, all flowering plants (also known as angiosperms) have seed coats that develop from the integuments of the ovule.
Let me know if you have any other questions! I’m always here to help explain the amazing world of plant biology.
See more here: What Do The Integuments In A Flower Develop Into The _____ In A Fruit? | In Flowering Plants The Integuments Of The Ovule Develop Into
Bio Ch38 Activities Quiz Flashcards | Quizlet
In flowering plants the integuments of the ovule develop into a(n) _____. seed coat ( The integuments of the ovule develop into a tough seed coat.) A carpel is composed of _____. Quizlet
Chapter 30 – Mastering Biology Flashcards | Quizlet
In flowering plants the integuments of the ovule develop into a(n) _____. cotyledon, seed coat, endosperm, sporophyte, fruit Quizlet
Ovule – Definition, Types, Components and Function
The ovule is made up of the nucellus, the integuments that form the outermost layer, and the female gametophyte (called an embryo sac in flowering plants), which are found at the very center. Biology Dictionary
Integuments in Plants – Definition, Types & Functions
Integuments in plants are the maternal tissues or having a maternal origin, as they originate from the ovular tissue or chalazal tissue (a part of the Biology Reader
Post-fertilization events: endosperm, embryo, seed, and fruit
The fertilized ovule, or seed, develops last, along with the transformation of the ovary into fruit. Here are some common features of seeds: Depending on the species of plant, a Khan Academy
Ovule – Definition, Functions, Development and Structure
Firstly, the ovule is a structure of a plant that develops into a seed during the fertilization process. A mature one contains food tissue, one or two future seed coats cover it, and we call them integuments. A small Toppr
32.8: Pollination and Fertilization – Development of the Seed
The seed, along with the ovule, is protected by a seed coat that is formed from the integuments of the ovule sac. In dicots, the seed coat is further divided into Biology LibreTexts
Ovule | Definition, Description, & Facts | Britannica
In angiosperms (flowering plants), one or more ovules are enclosed by the ovary, which develops into the fruit. Variations in form and position of the ovule are significant in plant classification: orthotropous ovules Britannica
14.4 Seed Plants: Angiosperms – Concepts of Biology
The ovary houses one or more ovules that will each develop into a seed upon fertilization. The male reproductive organs, the androecium or stamens, surround the central carpel. OpenStax
See more new information: charoenmotorcycles.com
Fertilisation In Flowering Plants -Class 12
Fertilisation And Seed Formation
How An Ovary Turns Into A Fruit | Sexual Reproduction In Flowering Plants | Khan Academy
Development Of Pollen Grains And Embryo Sac – Sexual Reproduction In Flowering Plants
Reproduction \U0026 Development In Plant
Angiosperms: Flowering Plants
Structure Of Anatropous Ovule
Flower Structures And Functions | Insect Pollinated Flowers
Reproduction 5 |The Marvels Of Fertilization In Flowering Plants
Link to this article: in flowering plants the integuments of the ovule develop into.
See more articles in the same category here: https://charoenmotorcycles.com/how