Are tool and die makers in demand?
Overall employment of machinists and tool and die makers is projected to show little or no change from 2022 to 2032. Despite limited employment growth, about 38,200 openings for machinists and tool and die makers are projected each year, on average, over the decade.
How long does it take to become a tool and die maker?
To pursue a career as a journeyman tool and die maker, you typically need to complete an apprenticeship. Most apprentices earn a degree or certificate from a vocational school before receiving on-the-job training from an employer. The process from apprentice to journeyman usually takes at least five years.
What is the difference between a tool maker and a die maker?
Toolmakers and die makers have similar roles. A die maker is a specialist category of toolmakers. A toolmaker makes tools for manufacturing through a machining process, utilizing equipment like mill machines, jig grinders, and lathes.
Is tool and die a skilled trade?
Tool and die makers are skilled artisans who enter their careers after a combination of education and hands-on training.
Is a toolmaker an engineer?
A toolmaker is a highly-skilled engineer who makes the precision tools which manufacturers use to create their parts or products. The in-depth toolmaker definition: A toolmaker is a highly-skilled engineer who is responsible for making precision tools, dies, moulds, jigs, holding devices and guides.
What is the best course after tool and die making?
What is the best course after Tool and Die Making? At the bachelor level, BTech in mechanical engineering are most pursued course for tool and die making or related jobs.
What is the average age of a machinist?
Demographic information on Machinists in the US. The workforce of Machinists in 2022 was 346,803 people, with 4.26% woman, and 95.7% men. The average age of male Machinists in the workforce is 45.5 and of female Machinists is 45.6, and the most common race/ethnicity for Machinists is White.
What do you call a tool and die maker?
Also called: Tool and Die Machinist, Tool and Die Maker, Tool and Fixture Specialist, Tool Maker. What they do: Analyze specifications, lay out metal stock, set up and operate machine tools, and fit and assemble parts to make and repair dies, cutting tools, jigs, fixtures, gauges, and machinists’ hand tools.
Is tool and die a CNC?
Machinists normally operate CNC machines, but tool and die makers often are trained to both operate CNC machines and write CNC programs and thus may do either task. There are multiple ways for workers to gain competency in the job as a machinist or tool or die maker.
Do tool and die makers weld?
After creating machine parts or tools, tool and die makers weld parts together to complete their assembly and correct errors in design.
How long does it take to be a tool and die maker?
It typically takes 3-5 years to become a tool and die maker: Year 1-2: Obtain a certificate in a relevant field, such as mechanical engineering or machining technology.
How many tool and die makers are in the US?
The Tool & die makers workforce in 2022 was 54,328 people (2.41% women and 97.6% men). This implies an average annual growth of −3.8% between 2014 (56,473) and 2022 (54,328).
What are the basic knowledge of a tool die maker?
This process consists of cutting, forming, stamping, and forging metals to create materials that vary in shape, size, and function. Tool and die manufacturing also involves the production of metal molds to shape plastics, ceramics, and other materials for traditional and injection molding.
Is tool and die making a good career?
You can make extremely good money being a tool and die maker. That’s just not well-known. As long as you’re willing to work — you have to be willing to work, that’s the thing — and you will get dirty, I’m not gonna lie.
How to become a tool and die maker?
Machinists typically have a high school diploma or equivalent, whereas tool and die makers may need to complete courses beyond high school. High school courses in math, blueprint reading, metalworking, and drafting are considered useful.
What is a toolmaker’s job?
A toolmaker is responsible for making precision tools (such as jigs, moulds and dies), special guides and holding devices, which are then used in the manufacturing process to make products. For example, a toolmaker might make the parts used on a car assembly line, or the part of a machine that fills a chocolate shell.
Who is known as tool maker?
Homo habilis was also known as tool maker because it was the first human who made weapons and tools from rocks. they also made equipment made of wood and some perishable items which have perished.
What is tool and tool engineering?
noun. the branch of engineering having to do with planning the tooling and processes required for manufacturing certain products, with the design and manufacture of the tools, dies, and jigs required, and with the control of the production processes.
What is the scope of Tool and Die Maker?
These professionals repair, build, and maintain tools and fixtures in compliance with production standards and safety regulations. Tool and die makers work in manufacturing and industrial environments, usually in factories and tool rooms, and primarily report to their supervisors and shift managers.
What is tool and die diploma?
Diploma in Mechanical Engineering (Tool & Die) is a 3-year bachelor’s degree program with 6 semesters. Puran Murti Polytechnic offers this course. The Diploma in Mechanical Engineering (Tool & Die) is related to the production and usage of making a design for the tool, production, and operation of machines.
What does a tool and die manager do?
Key Responsibilities: Supervises employees involved in the daily operations of Milling Machine Machinists, Aircraft Equipment Expeditors and or Dimension Control Technician SOW, fabrication of tools, building of jigs and fixtures, template and pattern making, and model building.
How stressful is being a machinist?
Machining could be a stressful job, but it is as stressful as you make it out to be. For example, there are many things to consider when machining parts, like quality issues, time deadlines, and machining conditions.
How long do machinists live?
Carpenters, masons and traders live from 45 to’ 50. Bankers, editors, jewelers, mannfacturers, mechanics, painters, shoemakers and tailors average from 40 to 45. Machinists, musi cians, and printers live from 35 to 40, and clerks, operatives and teachers are the shortest lived of all being, only from 30 to 35.
What is the scope of tool and die maker?
These professionals repair, build, and maintain tools and fixtures in compliance with production standards and safety regulations. Tool and die makers work in manufacturing and industrial environments, usually in factories and tool rooms, and primarily report to their supervisors and shift managers.
Will tool and die makers be automated?
While AI may automate certain tasks in tool and die making, the unique skills and capabilities of tool and die makers make them indispensable. It’s more likely that AI will augment their work, allowing them to focus on higher-level tasks and increasing their productivity.
What are the best courses after tool and die making?
Tool design, mechanical design, mechanical engineering, and Manufacturing engineering are great fields to apply your tool making experience too, and many companies will assist you in getting the formal training and college you need.
Is tool making a trade?
Generally, the time-frame to become competent in the trade of Tool and Die Maker is 8,000 hours (approximately four years) consisting of 7,280 hours of on-the job work experience and 720 hours of in-school training. An apprenticeship involves practical training provided on-the-job by a skilled worker, or trainer.
How much does a tool and die maker make in Canada?
How much does a tool and die maker III make?
How much do tool and die makers make in New York?
How much does an entry-level tool and die maker make?
Alright, let’s talk tool and die maker salary. You’re probably wondering how much you can earn, right? Well, it’s a great question, and the answer isn’t as straightforward as you might think. A tool and die maker’s salary can vary quite a bit depending on several factors, so let’s break it down.
Factors Affecting Tool and Die Maker Salary
Location: Where you work really matters. Big cities tend to have higher salaries compared to smaller towns. This is because of the cost of living and the demand for skilled workers.
Experience: Just like any job, the more experience you have, the more you’re likely to make. Entry-level tool and die makers might start off at a lower salary, but as they gain more skills and expertise, their earning potential increases.
Education and Certifications: Formal education and certifications can definitely boost your salary. A tool and die maker with a trade school certificate or an associate’s degree in tool and die making is often more sought after and can command a higher salary.
Industry: The specific industry you work in can also impact your earnings. For example, the aerospace industry or medical device manufacturing might offer higher salaries than working for a smaller, local company.
Company Size: Larger companies often have more resources and can afford to pay higher salaries, especially for experienced and highly skilled tool and die makers.
Union Membership: Being part of a union can sometimes lead to higher wages and benefits.
Overtime: Overtime hours are common in this field, and it can be a great way to boost your income. But keep in mind that working overtime can also lead to burnout, so it’s important to manage your time effectively.
Average Tool and Die Maker Salary
Now, let’s talk numbers. According to the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics, the median annual salary for tool and die makers in 2021 was $57,460, which translates to about $27.63 per hour. This means that half of all tool and die makers earned more than this amount, while the other half earned less.
Remember: This is just a median, and your actual salary can be higher or lower depending on those factors we talked about earlier.
Career Path and Earning Potential
Now, let’s talk about how you can grow your career and earn more as a tool and die maker.
Gain Experience: Start with an apprenticeship or entry-level position and build your skills and experience over time.
Pursue Certifications: Obtain relevant certifications, like those offered by the American Machinist’s Society or the National Tooling and Machining Association. This can make you more competitive in the job market.
Specialize in a Niche: Focus on a specific area of tool and die making like CNC machining or mold making. This can open up opportunities in high-demand industries.
Advance into Leadership Roles: As you gain experience and expertise, consider taking on leadership roles like supervisor, foreman, or even tool and die engineer.
FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions)
1. What kind of education do I need to be a tool and die maker?
You can start with a high school diploma, but a tool and die maker apprenticeship or an associate’s degree in tool and die making will give you a significant advantage.
2. What are some typical job responsibilities of a tool and die maker?
Tool and die makers are responsible for:
* Designing and creating tools and dies for various manufacturing processes
* Operating machine tools like lathes, mills, and grinders
* Maintaining and repairing tools and dies
* Following blueprints and specifications
* Working with engineers and other manufacturing staff
3. Is there a lot of demand for tool and die makers?
The demand for skilled tool and die makers is generally good. As manufacturing technology advances, there’s a growing need for experts who can design and maintain complex tools and dies.
4. What are some of the challenges of being a tool and die maker?
Tool and die making is a demanding field that requires physical strength, precision, and attention to detail. The work can be physically demanding and require working with heavy machinery.
5. What are some of the rewards of being a tool and die maker?
Tool and die makers play a vital role in the manufacturing process. They create the tools that make other products possible. It’s a rewarding career for those who enjoy problem-solving, working with their hands, and seeing tangible results.
6. What are some job titles that are related to tool and die making?
* Tool and Die Designer
* CNC Machinist
* Mold Maker
* Tool and Die Engineer
* Machinist
7. What are some good resources for learning more about tool and die making?
* The American Machinist’s Society (AMS)
* The National Tooling and Machining Association (NTMA)
* Your local technical college or vocational school
* Online courses and tutorials
Remember, tool and die making is a skilled trade, and it takes time, dedication, and continuous learning to excel in this field.
See more here: How Long Does It Take To Become A Tool And Die Maker? | Tool And Die Maker Salary
Tool and Die Maker Salaries by education, experience,
The average Tool And Die Maker salary in the United States is $82,523 as of May 28, 2024. The range for our most popular Tool And Die Maker positions (listed below) typically falls between $43,596 and $121,449. Salary.com
Tool and Die Maker Hourly Pay in 2024 | PayScale
The average hourly pay for a Tool and Die Maker is $27.05 in 2024. Visit PayScale to research tool and die maker hourly pay by city, experience, skill, employer Payscale
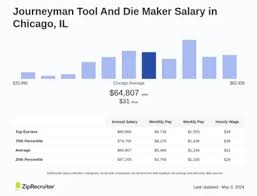
Tool And Die Maker Salary (May 2024) – Zippia
Tool and die maker salaries typically range between $41,000 and $68,000 yearly. The average hourly rate for tool and die makers is $25.46 per hour. Tool and die Zippia
Tool and Die Maker Salary | Salary.com
The base salary for Tool and Die Maker ranges from $62,817 to $79,047 with the average base salary of $71,002. The total cash compensation, which includes base, and annual Salary.com
Salary: Tool And Die Maker in United States 2024
The average salary for a Tool And Die Maker is $74,109 per year in United States. Salaries estimates are based on 675 salaries submitted anonymously to Glassdoor
Machinists and Tool and Die Makers – U.S. Bureau of
The median annual wage for tool and die makers was $61,490 in May 2023. Job Outlook. Overall employment of machinists and tool and die makers is projected to show little or no change from 2022 to U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics
Tool and Die Maker III Salary | Salary.com
The average Tool and Die Maker III salary in the United States is $80,452 as of May 28, 2024, but the range typically falls between $70,349 and $89,824. Salary ranges can salary.com
Salary: Tool Die Maker in United States 2024 | Glassdoor
The estimated total pay for a Tool And Die Maker is $90,447 per year in the United States area, with an average salary of $70,508 per year. These numbers Glassdoor
Tool and die maker salary ‐ CareerExplorer
Tool and die makers earn an average yearly salary of $37,278. Wages typically start from $24,589 and go up to $56,515. 41% below national average Updated in 2023. In this CareerExplorer
Tool And Die Maker Salary (Actual 2024 | Projected 2025)
Salaries range from $56,000 to $85,400 . The average Tool And Die Maker Hourly Wage is $25.00 per hour. Hourly wages range from $20.00 to $30.02 . Salaries and wages Velvet Jobs
See more new information: charoenmotorcycles.com
Considering Careers: Tool \U0026 Die Maker Apprentice
Job Talks Oyap – Tool \U0026 Die Maker Apprentice
Tool And Die Engineering
Tool And Die Maker Jobs
Job Talks – Tool And Die Maker – Randy Discusses Misconceptions Of The Job
Paid To Learn: Consider A Toolmaker Apprenticeship
Tbn Careers: Tool \U0026 Die/Machinist Jobs
Toolmakers Vs Machinists: What’S The Difference?
Advanced Apprenticeship – Toolmaker And Tool And Die Maintenance Technician
Link to this article: tool and die maker salary.
See more articles in the same category here: https://charoenmotorcycles.com/how