What is the term for the location where the windpipe bifurcates?
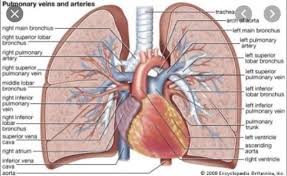
The trachea is a midline structure and lies just anterior the esophagus. After it originates from the larynx, the trachea divides into the left and right mainstem bronchi. This junction point is called the carina.
What tubes differ from the windpipe?
The lower respiratory tract consists of the trachea (windpipe), bronchial tubes, and lungs. The bronchial tubes carry air into the lungs and branch into smaller and smaller bronchioles.
What are the two tubes called that lead to the lungs?
Further down, the trachea divides into two tubes (left and right) called bronchi (BRAHN-kye). The bronchi connect the trachea to the lungs.
What is the space between the lungs called?
Your mediastinum is the space between these two pleural cavities. Your mediastinum is the middle section of your thoracic cavity. It’s located between your two pleural cavities (left and right).
What are the tubes that bifurcate from the windpipe or trachea?
The bronchi (singular. bronchus) extend from the trachea (also called the “windpipe”). [2] Together, these two structures form the tracheobronchial tree of the lungs. The trachea is the trunk of the tree located in the superior mediastinum.
What are the tubes the trachea bifurcates into?
At the level of the sternal angle, the trachea bifurcates into the right and left main bronchi. They undergo further branching to produce the secondary bronchi. Each secondary bronchi supplies a lobe of the lung, and gives rise to several segmental bronchi.
What is the tube that is also known as the windpipe?
Your trachea (TRAY-kee-uh) is a long, U-shaped tube that connects your larynx (voice box) to your lungs. The trachea is often called the windpipe.
What are the tubes in your throat called?
Sometimes you may swallow and cough because something “went down the wrong pipe.” The body has two “pipes.” The trachea (windpipe) is what connects the throat to the lungs. The esophagus is what connects the throat to the stomach.
What are the two tubes at the bottom of the trachea?
At the bottom of the trachea (say: TRAY-kee-uh), or windpipe, there are two large tubes. These tubes are called the main stem bronchi (say: BRONG-kye), and one heads left into the left lung, while the other heads right into the right lung.
What are the smaller tubes in the lungs called?
In your lungs, the main airways, called bronchi, branch off into smaller and smaller passageways. The smallest airways, called bronchioles, lead to tiny air sacs called alveoli.
What is another name for windpipe?
Also called trachea. Anatomy of the respiratory system showing the trachea, the right and left lungs and their lobes, and the bronchi.
What are the two tubes that enter each lung?
The trachea divides into the two main BRONCHI (tubes), one for each lung. The bronchi, in turn, subdivide further into bronchioles.
What is the space around the lung called?
The pleural cavity is a space between the visceral and parietal pleura. The space contains a tiny amount of serous fluid, which has two key functions. The serous fluid continuously lubricates the pleural surface and makes it easy for them to slide over each other during lung inflation and deflation.
What is the space that separates the lungs?
Within the thoracic cavity, the lungs are separated from the thoracic wall by the visceral and parietal pleurae. Between these two layers exists a potential space called the pleural cavity.
What separates the two lungs?
The lungs are separated by the mediastinum. This area contains the heart, trachea, esophagus, and many lymph nodes. The lungs are covered by a protective membrane known as the pleura and are separated from the abdominal cavity by the muscular diaphragm.
What tubes bifurcate into the lungs?
Bronchi and Bronchial Tree In the mediastinum, at the level of the fifth thoracic vertebra, the trachea divides into the right and left primary bronchi. The bronchi branch into smaller and smaller passageways until they terminate in tiny air sacs called alveoli.
What are two large tubes branching from the windpipe?
The bronchi are the two large tubes that carry air from your windpipe to your lungs. You have a left and right main bronchus in each lung. After the main bronchi, these tubes branch out into segments that look like tree branches.
What is the bifurcation of the trachea called?
Answer and Explanation: The bifurcation of the trachea is known as the carina. The trachea splits into the left and right primary bronchus at the position of the sternal angle and the fifth thoracic vertebra, or two vertebrae lower or higher, depending on changes in lung volume brought on by breathing.
What bifurcate from the windpipe?
The trachea and bronchi collectively form the tracheobronchial tree. The thoracic part divides at the tracheal bifurcation into the right and left main bronchi.
What tubes bifurcate from the larynx?
The trachea originates at the caudal end of the larynx and extends into the thoracic cavity, bifurcating distally at the carina to form the primary, extrapulmonary, airways of the lungs. The epithelium of the trachea is similar to that of the respiratory epithelium of the nasal cavity and the distal larynx.
What is the 4 bifurcation of the trachea?
The most inferior portion of the trachea, the bifurcation, is called the carina. It lies slightly to the right of the midline at the level of the fourth or fifth thoracic vertebra posteriorly and sternomanubrial junction anteriorly.
What is the tube in the trachea?
The trachea divides into two tubes as it goes into the chest. The tubes are called the right and left main stem bronchi (BRONK eye). Like branches on a tree, the two branches of the trachea divide into smaller tubes and end in the air sacs.
What is the pharyngeal tube?
Anatomy of the pharynx. The pharynx is a hollow, muscular tube inside the neck that starts behind the nose and opens into the larynx and esophagus. The three parts of the pharynx are the nasopharynx, oropharynx, and hypopharynx.
What is the tube from the larynx?
The laryngeal tube (LT) consists of a single-lumen reusable or disposable tube with a pharyngeal and oesophageal cuff which seals the pharyngeal airway and also the oesophageal inlet, and a ventilation outlet in between.
What separates food pipe and windpipe?
A small muscular flap (epiglottis) closes to prevent food and fluids from going down the windpipe (trachea) toward the lungs.
What is the windpipe called?
Your trachea, or windpipe, is one part of your airway system. Airways are pipes that carry oxygen-rich air to your lungs. They also carry carbon dioxide, a waste gas, out of your lungs.
What separates the trachea and esophagus?
A small muscular flap called the epiglottis closes to prevent food and liquid from going down the “wrong pipe” — your windpipe (trachea).
What is the bifurcation of the trachea called?
(i) The point of bifurcation of the trachea is called carina and is at the level of 5th thoracic vertebra.
Where is tracheal bifurcation located?
The bifurcation can be located anywhere between the levels of the fourth and seventh thoracic vertebrae. Most commonly it is located at the level of the sternal angle and vertebra T5.
Where is the location of the windpipe?
It’s behind the notch at your lower throat, between the inside edges of your collarbones. In a diagram of your trachea and other respiratory organs, you can see the trachea between the top lobes of the lungs. It’s in front of your esophagus (tube that carries food from your mouth to your stomach).
What is the term for the bifurcation of the trachea?
The most inferior portion of the trachea, the bifurcation, is called the carina. It lies slightly to the right of the midline at the level of the fourth or fifth thoracic vertebra posteriorly and sternomanubrial junction anteriorly.
What is the function of the windpipe in inhalation and exhalation?
What is tracheal bifurcation?
How does a windpipe purify air?
How does bronchial bifurcation work?
Let’s get into the details. Imagine your windpipe, also known as the trachea, as a big, hollow tube that carries air to and from your lungs. When it reaches your chest, it splits into two tubes, like a Y-shaped fork in the road. These tubes are the primary bronchi.
The right primary bronchus goes to your right lung, and the left primary bronchus goes to your left lung. Now, if you look at them closely, you’ll see that they’re not exactly the same. The right bronchus is a bit wider and shorter than the left one. This is because your right lung is a bit bigger than your left lung.
But hold on, the story doesn’t end here. Each of these primary bronchi branches out further, like the branches of a tree. They keep splitting into smaller and smaller tubes called secondary bronchi and then tertiary bronchi. Think of them as smaller highways that connect to different parts of your lungs.
These bronchioles are the tiniest tubes in your respiratory system. They are so small that they only have a single layer of cells. Imagine how thin that is! These bronchioles end in tiny air sacs called alveoli. The alveoli are where the magic happens – that’s where oxygen is absorbed into your bloodstream and carbon dioxide is released from your blood.
Think of your lungs as a big, intricate network of tubes. It’s all about getting air to your alveoli, and that air is essential for your body to function.
The Importance of the Tubes
Now, let’s talk about why these tubes are so important.
* Airflow: They act as a passageway for air to travel in and out of your lungs.
* Filtering: As air moves through the bronchi, it’s cleaned and warmed. The mucus lining of your bronchi traps dust, dirt, and other pollutants that you breathe in.
* Protection: Tiny hair-like structures called cilia line the bronchi and move in a wave-like motion. This helps to sweep out any trapped debris.
* Gas Exchange: The alveoli at the end of these tubes are responsible for the crucial exchange of gases between your blood and the air you breathe.
What can go wrong?
But what happens when these tubes aren’t working properly? There are a few things that can go wrong, and they can cause all kinds of problems.
Here are some common issues:
* Asthma: This condition causes your bronchi to become inflamed and narrow, making it difficult to breathe.
* Bronchitis: This is an infection that inflames the lining of your bronchi, causing a cough and mucus production.
* Pneumonia: An infection that can affect your lungs, including the bronchi, causing inflammation and fluid buildup.
* Lung Cancer: This is a serious condition where abnormal cells grow in your lungs, and can even spread to other parts of your body.
How can we keep our tubes healthy?
Well, you can do your part to keep your bronchi healthy by:
* Not smoking: Smoking irritates your bronchi and increases your risk of lung disease.
* Getting vaccinated: Vaccines can help to prevent infections that can affect your lungs.
* Washing your hands: This is important to prevent the spread of germs that can cause respiratory infections.
* Getting regular exercise: Exercise helps to strengthen your lungs and improve your overall health.
FAQs
1. Why are the bronchi important for breathing?
The bronchi are crucial for breathing because they act as the passageways that carry air to and from the lungs. They also help to clean and warm the air, and they play a role in gas exchange.
2. What is the difference between the right and left bronchi?
The right bronchus is wider and shorter than the left bronchus. This is because the right lung is slightly larger than the left lung.
3. What happens if the bronchi become blocked?
If the bronchi become blocked, it can make it difficult or impossible to breathe. This can happen due to conditions like asthma, bronchitis, or pneumonia.
4. How can I prevent problems with my bronchi?
You can prevent problems with your bronchi by avoiding smoking, getting vaccinated, washing your hands regularly, and exercising regularly.
5. What are the symptoms of bronchi problems?
Symptoms of bronchi problems can include coughing, shortness of breath, wheezing, and chest pain.
6. What are some common treatments for bronchi problems?
Treatments for bronchi problems can include medications like bronchodilators to open up the airways, antibiotics for bacterial infections, and corticosteroids to reduce inflammation.
Remember, your bronchi are essential for your health. Take care of them, and they’ll take care of you!
See more here: What Tubes Differ From The Windpipe? | Tubes That Bifurcate From The Windpipe
Chapter 12 Flashcards | Quizlet
Study with Quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like Tubes that bifurcate from the windpipe: a. Alveoli b. Bronchioles c. Sinuses d. Adenoids e. Bronchi, Uppermost portion of the lung: a. Hilum b. Apex c. Base d. Lobe e. Quizlet
Trachea: Anatomy, blood supply, innervation and function | Kenhub
The trachea, or windpipe, is a fibrocartilaginous tube that connects the larynx and the lungs. It divides into two main bronchi at the tracheal bifurcation, which is Kenhub
Trachea: Main Function and Common Problems
The trachea (also called the windpipe) is the large tube that brings air from the nasal passages, throat, and larynx (the upper respiratory tract) to the two large airways that branch off into each lung Verywell Health
The Tracheobronchial Tree – Trachea – Bronchi
Learn about the trachea, bronchi and bronchioles, the airways that allow air to enter the lungs. Find out how they branch, what they are made of, and how they are innervated and supplied. TeachMeAnatomy
Trachea (Windpipe): Function and Anatomy – Cleveland Clinic
The trachea is the long, U-shaped tube that connects your larynx to your lungs. It’s part of your respiratory system and helps you breathe. Learn about its Cleveland Clinic
Trachea (Windpipe) Definition, Anatomy, Function,
Learn about the trachea, the largest airway in the respiratory system that connects the larynx to the bronchi. Find out where it is located, what it is made of, how it works, and what problems can The Respiratory System
Bronchi: Anatomy, function and histology | Kenhub
Learn about the bronchi, the airways that branch from the trachea (windpipe) into the lungs. Find out how they are structured, what they do, and how they are affected by diseases. Kenhub
Tracheobronchial Anatomy | SpringerLink
The trachea is a flexible cylindrical tube composed of cartilaginous incomplete rings, connected by a fibromuscular membrane and lined internally by Springer
See more new information: charoenmotorcycles.com
Ap2: Respiratory System: Epiglottis
Food Going Down The Wrong Tube
Parts Of A Tracheostomy Tube
The Inside Of A Human \”Windpipe\”
What Is A Fenestrated Tracheostomy Tube? Essential Info \U0026 Faqs. Life With A Vent
Suctioning 101: Essential Info \U0026 Tips! Life With A Vent
Tracheostomy Components
Have A Trach \U0026 Vent? Info You Need To Know! Life With A Vent
What You Need To Know About Tracheostomy Tubes
Link to this article: tubes that bifurcate from the windpipe.
See more articles in the same category here: https://charoenmotorcycles.com/how