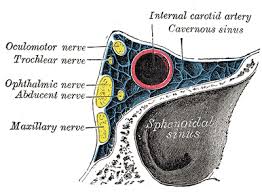
What does the infratrochlear nerve do?
It provides sensory innervation to the medial upper and lower eyelids, the skin of the lateral part of the nose (external) above the medial canthus, medial conjunctiva, and lacrimal apparatus, including the caruncle.
What is the Infratrochlear and external nasal nerve?
The infratrochlear nerve (external nasal), a branch of which goes to the lacrimal canal and the medial eyelid. It can be palpated below the trochlea. The supratrochlear nerve. This branch is also called the ethmoidal filament for the cribriform plate, over which it passes.
What is the function of the lacrimal nerve?
The lacrimal nerve provides sensory innervation to: the lacrimal gland. a small area of skin over the lateral portion of the upper eyelid. both surfaces (i.e. ocular and palpebral ) of the conjunctiva at the lateral portion of the upper eyelid (i.e. the conjunctiva at the superior fornix )
What does the infratrochlear nerve affect quizlet?
Infratrochlear nerve. Affects the skin of the lower lip and chin. Mental nerve. Affects the point and lower side of the nose.
How do you block the infratrochlear nerve?
The infratrochlear nerve can be blocked by infiltrating at the superomedial border of the orbit and along its medial wall. The external nasal branch of the anterior ethmoidal nerve can also be blocked by infiltration at the junction of the nasal bone and the nasal cartilage.
What does the nasal nerve do?
The external nasal nerve also arises from the nasociliary and exits between the border of the nasal bone and the upper lateral cartilage, providing sensation to the skin of the nasal tip, the medial aspect of the nasal alae, and the dorsum of the nose.
What does the infraorbital nerve do?
The infraorbital nerve supplies sensory innervation to the lower eyelid, the side of the nose, and the upper lip (see image below). Since the infraorbital nerve provides a considerably large area of sensory innervation, it is a prime candidate for a regional nerve block.
What is the nerve from the nose to the eye?
The nasociliary nerve provides sensory information to the cornea, eyelids, and the cells of the nasal cavity. The nasociliary nerve is often involved in nasal pain. Nasal pain is rare and can happen spontaneously, as a result of injury, or as a side effect of surgery on the nose.
What happens if the lacrimal nerve is damaged?
If the nerve fibers are destroyed, injured or severed, the sensitivity of the cornea and thus the regulation of tears is disturbed.
Is lacrimal nerve sympathetic or parasympathetic?
The lacrimal gland receives sensory, parasympathetic, as well as sympathetic innervation. The lacrimal nerve, from the ophthalmic branch of the trigeminal nerve provides sensory innervation to the gland. Parasympathetic secretomotor neurons stimulate the secretion of lacrimal fluid.
Which nerve causes lacrimation?
The lacrimatory nucleus receives information related to emotional responses from the hypothalamus. Information from the sensory nuclei of the trigeminal nerve is also received by the lacrimatory nucleus, which brings about reflex lacrimation upon irritation of the cornea or conjunctiva.
What is the function of infratrochlear nerve?
The infratrochlear nerve provides sensory innervation to the skin of the inferior medial canthus and lateral nose, conjunctiva, caruncle, and lacrimal sac. The lacrimal nerve supplies the lacrimal gland, the lateral upper lid and conjunctiva.
What are the 3 eye nerves?
Three of these cranial nerves, cranial nerve III (3), cranial nerve IV (4) and cranial nerve VI (6) are responsible for all of the eye’s movements. Problems with these nerves can cause issues with eye position and movement including eyes turning in, turning out, or being vertically misaligned or causing double vision.
What happens if the supraorbital nerve is damaged?
Supraorbital Nerve Pain If there is damage to the supraorbital nerve, you may experience supraorbital neuralgia (nerve pain) with pain above your eyebrow, and possibly extending to the scalp. The hallmarks of supraorbital neuralgia, a rare condition, include: Forehead pain.
What motor nerve controls chewing?
The trigeminal nerve is also known as cranial nerve 5 or the fifth cranial nerve. It provides sensations to your scalp and face. It also controls some muscles involved in chewing and swallowing.
What nerve affects the muscles of the chin and lower lip?
The mental nerve will provide sensory innervation to the anterior territory of the buccal mucosa, lower lip, and the skin of the chin ventral to its foramen.
How to clear nerve blockage?
Some injections provide prolonged pain relief. An injection of anti-inflammatory medication in addition to local anesthetic may allow the damaged nerves to heal by relieving the inflammation. Nerves are like cables that carry electrical signals between your brain and the rest of your body and vice versa.
How do you sleep after a nerve block?
You may feel some mild breathing discomfort. This goes away as the block wears off. If you have breathing discomfort, rest and sleep with your head and upper body resting on 2 to 3 pillows. It may also help to sit in a recliner, with your upper body raised.
Why is my hand hot after a nerve block?
Conclusions: Forearm nerve blocks produce a chemical sympathectomy that provides a significant increase in skin temperature as a result of vasodilatation in most patients. They also provide prolonged finger numbness.
What nerve makes your nose run?
When the trigeminal nerve is stimulated, it increases the amount of mucus the sinuses and nasal lining produce, causing you to sneeze and/or experience a runny nose.
Are eye and nose nerves connected?
In the orbit, the ophthalmic nerve (Fig. 10-32) divides into three branches. The nasociliary nerve travels along the medial orbital roof, where it branches into the nasal cavity.
What happens if the infraorbital nerve is damaged?
Injury to the infraorbital nerve can be caused by trauma, including various facial fractures. Due to this nerve injury, patients complain of numbness and pain in the entire cheek, the ala of nose, and upper lip. In general, spontaneous sensory recovery is expected after decompressive surgery.
What are the risks of infraorbital nerve block?
It is possible for a patient to develop an allergic reaction to the anesthetic medication used for the procedure. Other reactions to the anesthetic medication include cardiovascular and neurological symptoms. Depending on the anesthetic, methemoglobinemia is also a possible complication.
How long does it take for the infraorbital nerve to heal?
The majority of the patients with ZMC fractures and neurosensory deficits of the infraorbital nerve, when treated with open reduction and internal fixation, have complete recovery of the neurosensory deficits by the end of six months postoperatively.
What does the infraorbital nerve do?
The infraorbital nerve supplies sensory innervation to the lower eyelid, the side of the nose, and the upper lip (see image below). Since the infraorbital nerve provides a considerably large area of sensory innervation, it is a prime candidate for a regional nerve block.
What is the action of the supraorbital nerve?
The supraorbital nerve exits the frontal bone through the supraorbital foramen and provides sensation to the superior aspects of the eye and the forehead and, extending posteriorly, provides cutaneous coverage to a large portion of the scalp.
What happens if the supraorbital nerve is damaged?
Supraorbital Nerve Pain If there is damage to the supraorbital nerve, you may experience supraorbital neuralgia (nerve pain) with pain above your eyebrow, and possibly extending to the scalp. The hallmarks of supraorbital neuralgia, a rare condition, include: Forehead pain.
What does the facial nerve do for the eye?
The facial nerve performs these motor (movement) and sensory functions: Controls the muscles that make your facial expressions. Controls muscle in your inner ear that moderates loudness of sound.
What is the infratrochlear nerve?
What is the impact of infratrochlear nerve damage?
Where does the infratrochlear nerve travel?
How is the infratrochlear nerve blocked?
What Does the Infratrochlear Nerve Affect?
The infratrochlear nerve, also known as the nasociliary nerve, is a branch of the ophthalmic nerve, which itself is a part of the trigeminal nerve (the fifth cranial nerve).
Think of it like this: the trigeminal nerve is the big boss, the ophthalmic nerve is the manager, and the infratrochlear nerve is a team member responsible for specific tasks.
The infratrochlear nerve travels through the orbit, the bony socket that holds the eyeball, and reaches the medial aspect of the eye. This means it’s responsible for sensation in the following areas:
The skin of the medial (inner) part of the upper eyelid. Imagine you’re looking straight ahead. The inner corner of your eye, where your tear duct is, is where the infratrochlear nerve handles sensation.
The conjunctiva of the medial part of the eye. The conjunctiva is the transparent membrane that covers the white part of your eye and the inner surface of your eyelid.
The skin of the medial part of the nose. That part of your nose right between your eyes? That’s where the infratrochlear nerve takes care of feeling.
The lacrimal sac. This is a small pouch located in the inner corner of the eye that collects tears.
The infratrochlear nerve also supplies motor innervation to the dilator muscle of the pupil, which helps regulate the size of the pupil.
In simpler terms, the infratrochlear nerve is like a tiny conductor for sensation and movement in the inner corner of the eye and the nose. It makes sure everything feels and functions properly in that area.
What Happens if the Infratrochlear Nerve is Damaged?
If the infratrochlear nerve is damaged, you might experience several symptoms:
Loss of sensation: You might not be able to feel pain, temperature, or light touch in the areas it supplies. This is called anesthesia.
Pain: You might experience pain in the areas innervated by the nerve. This is called neuralgia.
Abnormal pupil dilation: The pupil might become larger than usual, a condition known as mydriasis.
It’s important to note that damage to the infratrochlear nerve is relatively uncommon. It usually occurs as a result of trauma, such as a blow to the face, or surgery in the area.
What Causes Damage to the Infratrochlear Nerve?
Here are some common causes of infratrochlear nerve damage:
Trauma: A direct blow to the face, especially the area around the eye, can damage the nerve.
Surgery: Surgery in the area around the eye, such as sinus surgery or eye surgery, can also damage the nerve.
Infection: Infections of the face, such as sinusitis or cellulitis, can sometimes affect the nerve.
Tumors: Tumors in the area around the eye can also put pressure on the nerve and cause damage.
Diagnosing Infratrochlear Nerve Damage
A doctor can diagnose infratrochlear nerve damage by performing a physical exam and asking about your symptoms. They might also order imaging tests, such as a CT scan or MRI, to rule out other conditions.
Treating Infratrochlear Nerve Damage
The treatment for infratrochlear nerve damage depends on the cause. If the damage is caused by trauma, the nerve may heal on its own. If the damage is caused by surgery, it may require additional surgery to repair the nerve.
Sometimes, doctors may recommend medication to manage pain and inflammation.
In most cases, however, the symptoms of infratrochlear nerve damage are temporary and resolve on their own within a few weeks or months.
FAQs
What are the symptoms of infratrochlear nerve damage?
The most common symptom is loss of sensation in the area around the inner corner of the eye and the nose. You might also experience pain, burning, or tingling in the affected area.
How is infratrochlear nerve damage diagnosed?
A doctor will typically diagnose infratrochlear nerve damage based on your symptoms and a physical exam. They may also order imaging tests to rule out other conditions.
How is infratrochlear nerve damage treated?
Treatment depends on the cause of the damage. In some cases, the nerve may heal on its own. In other cases, medication or surgery may be necessary.
What can I do to prevent infratrochlear nerve damage?
The best way to prevent infratrochlear nerve damage is to avoid injury to the face. Wear protective eyewear when playing sports or doing other activities that could put your eyes at risk.
How long does it take for infratrochlear nerve damage to heal?
The time it takes for infratrochlear nerve damage to heal depends on the severity of the damage and the underlying cause. In some cases, the nerve may heal within a few weeks or months. In other cases, it may take longer or not heal at all.
Final Thoughts
The infratrochlear nerve is a small but important part of our nervous system. It helps us to feel and move the inner corner of our eye and the nose. While damage to this nerve is relatively uncommon, it can cause a variety of symptoms. If you’re experiencing any symptoms of infratrochlear nerve damage, it’s important to see a doctor for diagnosis and treatment.
See more here: What Is The Infratrochlear And External Nasal Nerve? | What Does The Infratrochlear Nerve Affect
Neuroanatomy, Infratrochlear Nerve – StatPearls
The infratrochlear nerve is a branch of the nasociliary nerve, which forms part of the ophthalmic division of the trigeminal nerve (V1). It provides sensory innervation to the medial upper and lower National Center for Biotechnology Information
Infratrochlear Nerve – an overview | ScienceDirect Topics
The infratrochlear nerve arises from the nasociliary nerve close to the anterior ethmoidal foramen. It courses anteriorly along the inner wall of the orbit, above ScienceDirect
Infratrochlear Nerve | Complete Anatomy – Elsevier
The infratrochlear nerve is a sensory nerve that conveys general sensation from the skin of the medial eyelids and bridge of the nose, the medial conjunctiva, and superficial Elsevier
Neuroanatomy, Infratrochlear Nerve – PubMed
The infratrochlear nerve is a branch of the nasociliary nerve, which forms part of the ophthalmic division of the trigeminal nerve (V1). It provides sensory PubMed
Infratrochlear nerve – Location, Structure, Function, Anatomy
The infratrochlear nerve is a small nerve that is a branch of the ophthalmic nerve, which is itself a branch of the trigeminal nerve. It is responsible for providing Anatomy.co.uk
Infratrochlear nerve | Radiology Reference Article | Radiopaedia.org
The infratrochlear nerve is an extraconal branch of the nasociliary nerve, a branch of ophthalmic division of the trigeminal nerve. Some authors describe it as the Radiopaedia
Infratrochlear nerve – e-Anatomy – IMAIOS
The infratrochlear nerve (n. infratrochlearis) is given off from the nasociliary just before it enters the anterior ethmoidal foramen. It runs forward along the upper border of the Rectus medialis, and is joined, IMAIOS
Unveiling the Infratrochlear Nerve: An Essential Player in
The infratrochlear nerve, a branch of the ophthalmic division of the trigeminal nerve, is a crucial contributor to facial sensation. Its anatomical course and functions highlight its DoveMed
Neuroanatomy, Infratrochlear Nerve – Abstract – Europe PMC
In particular, the infratrochlear nerve has an impact clinically for ENT surgeons and anesthetists. Embryology. The trigeminal ganglia are visible in week 4. It initially Europe PMC
See more new information: charoenmotorcycles.com
Infratrochlear Nerve – Know It All 🔊✅
What Does Infratrochlear Mean
Cn 5: Trigeminal Nerve (Scheme, Divisions, Pathway) | Neuroanatomy
What Does Infratrochlear Mean?
Branching Of The Ophthalmic Nerve And Artery
Sensory Nerves Of The Face (Trigeminal Nerve, Cn V Anatomy)
Anatomy Dissected: Cranial Nerve V (Trigeminal Nerve)
The Ophthalmic Nerve | Trigeminal Nerve Part Ii | Neuroanatomy
Neurology | Trigeminal Nerve: Cranial Nerve V
Link to this article: what does the infratrochlear nerve affect.
See more articles in the same category here: https://charoenmotorcycles.com/how